13.6: Humidity, Evaporation, and Boiling
- Page ID
- 1584
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the relationship between vapor pressure of water and the capacity of air to hold water vapor.
- Explain the relationship between relative humidity and partial pressure of water vapor in the air.
- Calculate vapor density using vapor pressure.
- Calculate humidity and dew point.
The expression “it’s not the heat, it’s the humidity” makes a valid point. We keep cool in hot weather by evaporating sweat from our skin and water from our breathing passages. Because evaporation is inhibited by high humidity, we feel hotter at a given temperature when the humidity is high. Low humidity, on the other hand, can cause discomfort from excessive drying of mucous membranes and can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections.

Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Dew drops like these, on a banana leaf photographed just after sunrise, form when the air temperature drops to or below the dew point. At the dew point, the rate at which water molecules join together is greater than the rate at which they separate, and some of the water condenses to form droplets. (credit: Aaron Escobar, Flickr)
When we say humidity, we really mean relative humidity. Relative humidity tells us how much water vapor is in the air compared with the maximum possible. At its maximum, denoted as saturation, the relative humidity is 100%, and evaporation is inhibited. The amount of water vapor in the air depends on temperature. For example, relative humidity rises in the evening, as air temperature declines, sometimes reaching the dew point. At the dew point temperature, relative humidity is 100%, and fog may result from the condensation of water droplets if they are small enough to stay in suspension. Conversely, if you wish to dry something (perhaps your hair), it is more effective to blow hot air over it rather than cold air, because, among other things, the increase in temperature increases the energy of the molecules, so the rate of evaporation increases.
The amount of water vapor in the air depends on the vapor pressure of water. The liquid and solid phases are continuously giving off vapor because some of the molecules have high enough speeds to enter the gas phase; see Figure(a). If a lid is placed over the container, as in Figure(b), evaporation continues, increasing the pressure, until sufficient vapor has built up for condensation to balance evaporation. Then equilibrium has been achieved, and the vapor pressure is equal to the partial pressure of water in the container. Vapor pressure increases with temperature because molecular speeds are higher as temperature increases. Table gives representative values of water vapor pressure over a range of temperatures.
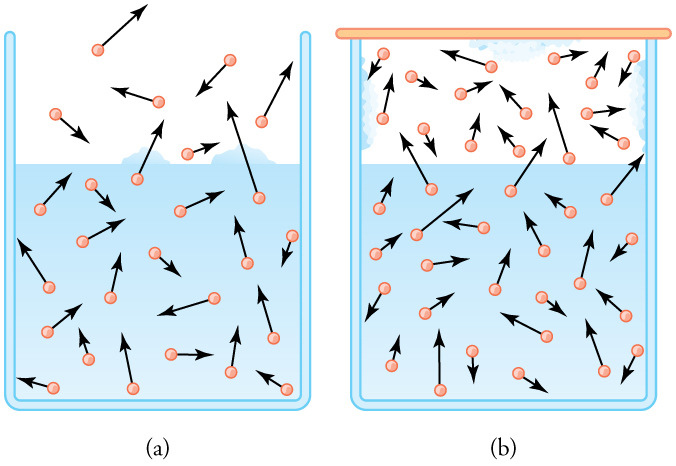
Relative humidity is related to the partial pressure of water vapor in the air. At 100% humidity, the partial pressure is equal to the vapor pressure, and no more water can enter the vapor phase. If the partial pressure is less than the vapor pressure, then evaporation will take place, as humidity is less than 100%. If the partial pressure is greater than the vapor pressure, condensation takes place. In everyday language, people sometimes refer to the capacity of air to “hold” water vapor, but this is not actually what happens. The water vapor is not held by the air. The amount of water in air is determined by the vapor pressure of water and has nothing to do with the properties of air.
| Temperature \(^oC\) | Vapor Pressure \((Pa)\) | Saturation vapor density \(g/m^3\) |
| −50 | 4.0 | 0.039 |
| -20 | \(1.04 \times 10^2\) | 0.89 |
| -10 | \(2.60 \times 10^2\) | 2.36 |
| 0 | \(6.10 \times 10^2\) | 4.84 |
| 5 | \(8.68 \times 10^2\) | 6.80 |
| 10 | \(1.19 \times 10^3\) | 9.40 |
| 15 | \(1.69 \times 10^3\) | 12.8 |
| 20 | \(2.33 \times 10^3\) | 17.2 |
| 25 | \(3.17 \times 10^3\) | 23.0 |
| 30 | \(4.24 \times 10^3\) | 30.4 |
| 37 | \(6.31 \times 10^3\) | 44.0 |
| 40 | \(7.34 \times 10^3\) | 51.1 |
| 50 | \(1.23 \times 10^4\) | 82.4 |
| 60 | \(1.99 \times 10^4\) | 130 |
| 70 | \(3.12 \times 10^4\) | 197 |
| 80 | \(4.73 \times 10^4\) | 294 |
| 90 | \(7.01 \times 10^4\) | 418 |
| 95 | \(8.59 \times 10^4\) | 505 |
| 100 | \(1.01 \times 10^5\) | 598 |
| 120 | \(1.99 \times 10^5\) | 1095 |
| 150 | \(4.76 \times 10^5\) | 2430 |
| 200 | \(1.55 \times 10^6\) | 7090 |
| 220 | \(2.32 \times 10^6\) | 10,200 |
Saturation Vapor Density of Water
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Calculating Density Using Vapor Pressure
Table gives the vapor pressure of water at .\(20.0^oC\) as \(2.33 \times 10^3 \, Pa\). Use the ideal gas law to calculate the density of water vapor in \(g/m^3\) that would create a partial pressure equal to this vapor pressure. Compare the result with the saturation vapor density given in the table.
Strategy
To solve this problem, we need to break it down into a two steps. The partial pressure follows the ideal gas law,
\[PV = nRT,\]
where \(n\) is the number of moles. If we solve this equation for \(n/V\)
to calculate the number of moles per cubic meter, we can then convert this quantity to grams per cubic meter as requested. To do this, we need to use the molecular mass of water, which is given in the periodic table.
Solution
1. Identify the knowns and convert them to the proper units:
- temperature \(T = 20^oC = 203 \, K\)
- vapor pressure \(P\) of water at \(20^oC\) is \(2.33 \times 10^3 \, Pa\)
- molecular mass of water is \(18.0 \, g/m\)
2. Solve the ideal gas law for \(n?V\).
\[\dfrac{n}{V} = \dfrac{P}{RT}\]
3. Substitute known values into the equation and solve for \(n/V\).
\[\dfrac{n}{V} = \dfrac{P}{RT} = \dfrac{2.33 \times 10^3 \, Pa}{(8.31 \, J/mol \cdot K)(293 \, K)} = 0.957 \, mol/m^3\]
4. Convert the density in moles per cubic meter to grams per cubic meter.
\[\rho = \left(0.957\dfrac{mol}{m^3}\right)\left(\dfrac{18.0 \, g}{mol}\right) = 17.2 \, g/m^3\]
Discussion
The density is obtained by assuming a pressure equal to the vapor pressure of water at \(20.0^oC\). The density found is identical to the value in Table, which means that a vapor density of \(17.2 \, g/m^3\) at \(20.9^oC\) creates a partial pressure of \(2.33 \times 10^3 \, Pa\), equal to the vapor pressure of water at that temperature. If the partial pressure is equal to the vapor pressure, then the liquid and vapor phases are in equilibrium, and the relative humidity is 100%. Thus, there can be no more than 17.2 g of water vapor per \(m^3\) at \(20.0^oC\), so that this value is the saturation vapor density at that temperature. This example illustrates how water vapor behaves like an ideal gas: the pressure and density are consistent with the ideal gas law (assuming the density in the table is correct). The saturation vapor densities listed in Table are the maximum amounts of water vapor that air can hold at various temperatures.
Percent Relative Humidity
We define percent relative humidity as the ratio of vapor density to saturation vapor density, or
\[percent \, relative \, humidity = \dfrac{vapor \, density}{saturation \, vapor \, density} \times 100\]
We can use this and the data in Table to do a variety of interesting calculations, keeping in mind that relative humidity is based on the comparison of the partial pressure of water vapor in air and ice.
We can use this and the data in Table to do a variety of interesting calculations, keeping in mind that relative humidity is based on the comparison of the partial pressure of water vapor in air and ice.
Exampl \(\PageIndex{2}\): Calculating Humidity and Dew Point
(a) Calculate the percent relative humidity on a day when the temperature is \(25.0^oC\) and the air contains 9.40 g of vapor per \(m^3\). (b) At what temperature will this air reach 100% relative humidity (the saturation density)? This temperature is the dew point. (c) What is the humidity when the air temperature is \(25.0^oC\) and the dew point is \(-10.0^oC\)?
Strategy and Solution
(a) Percent relative humidity is defined as the ratio of vapor density to saturation vapor density.
\[percent \, relative \, humidity = \dfrac{vapor \, density}{saturation \, vapor \, density} \times 100\]
The first is given to be \(9.40 \, g/m^3\), and the second is found in Table to be \(23.0 \, g/m^3\). Thus,
\[percent \, relative \, humidity = \dfrac{9.40 \, g/m^3}{23.0 \, g/m^3} \times 100 = 40.9 \%\]
(b) The air contains \(9.40 \, g/m^3\) of water vapor. The relative humidity will be 100% at a temperature where \(9.40 \, g/m^3\) is the saturation density. Inspection of Table reveals this to be the case at \(10.0^oC\),
where the relative humidity will be 100%. That temperature is called the dew point for air with this concentration of water vapor.
(c) Here, the dew point temperature is given to be \(10.0^oC\). Using Table, we see that the vapor density is \(2.36 \, g/m^3\), because this value is the saturation vapor density at \(-10.0^oC\). The saturation vapor density at \(25.0^oC\) is seen to be \(23.0 \, g/m^3\). Thus, the relative humidity at \(25.0^oC\) is
\[percent \, relative \, humidity = \dfrac{2.36 \, g/m^3}{23.0 \, g/m^3} \times 100 = 10.3 \%\]
Discussion
The importance of dew point is that air temperature cannot drop below \(10.0^oC\) in part (b), or \(-10.0^oC\) in part (c), without water vapor condensing out of the air. If condensation occurs, considerable transfer of heat occurs (discussed in Heat and Heat Transfer Methods), which prevents the temperature from further dropping. When dew points are below \(0^oC\), freezing temperatures are a greater possibility, which explains why farmers keep track of the dew point. Low humidity in deserts means low dew-point temperatures. Thus condensation is unlikely. If the temperature drops, vapor does not condense in liquid drops. Because no heat is released into the air, the air temperature drops more rapidly compared to air with higher humidity. Likewise, at high temperatures, liquid droplets do not evaporate, so that no heat is removed from the gas to the liquid phase. This explains the large range of temperature in arid regions.
Why does water boil at \(100^oC\)? You will note from Table that the vapor pressure of water at \(100^oC\) is \(1.01 \times 10^5 \, Pa\), or 1.00 atm. Thus, it can evaporate without limit at this temperature and pressure. But why does it form bubbles when it boils? This is because water ordinarily contains significant amounts of dissolved air and other impurities, which are observed as small bubbles of air in a glass of water. If a bubble starts out at the bottom of the container at \(20^oC\), it contains water vapor (about 2.30%). The pressure inside the bubble is fixed at 1.00 atm (we ignore the slight pressure exerted by the water around it). As the temperature rises, the amount of air in the bubble stays the same, but the water vapor increases; the bubble expands to keep the pressure at 1.00 atm. At \(100^oC\), water vapor enters the bubble continuously since the partial pressure of water is equal to 1.00 atm in equilibrium. It cannot reach this pressure, however, since the bubble also contains air and total pressure is 1.00 atm. The bubble grows in size and thereby increases the buoyant force. The bubble breaks away and rises rapidly to the surface—we call this boiling! (See Figure.)

Check Your Understanding
- Freeze drying is a process in which substances, such as foods, are dried by placing them in a vacuum chamber and lowering the atmospheric pressure around them. How does the lowered atmospheric pressure speed the drying process, and why does it cause the temperature of the food to drop?
[Hide Solution]
Decreased the atmospheric pressure results in decreased partial pressure of water, hence a lower humidity. So evaporation of water from food, for example, will be enhanced. The molecules of water most likely to break away from the food will be those with the greatest velocities. Those remaining thus have a lower average velocity and a lower temperature. This can (and does) result in the freezing and drying of the food; hence the process is aptly named freeze drying.
PHET EXPLORATIONS: STATES OF MATTER
Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. Add or remove heat and watch the phase change. Change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure-temperature diagram respond in real time. Relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules.

Summary
- Relative humidity is the fraction of water vapor in a gas compared to the saturation value.
- The saturation vapor density can be determined from the vapor pressure for a given temperature.
- Percent relative humidity is defined to be \[percent \, relative \, humidity = \dfrac{vapor \, density}{saturation \, vapor \, density} \times 100\%\]
- The dew point is the temperature at which air reaches 100% relative humidity.
Glossary
- dew point
- the temperature at which relative humidity is 100%; the temperature at which water starts to condense out of the air
- saturation
- the condition of 100% relative humidity
- percent relative humidity
- the ratio of vapor density to saturation vapor density
- relative humidity
- the amount of water in the air relative to the maximum amount the air can hold


