2.11: Phase Transitions and Phase Equilibria
- Page ID
- 18863
\( \newcommand\bes{\begin{equation}\begin{split}}\)
\( \newcommand\ltwid{\propto}\)
\( \newcommand\ees{\end{split}\end{equation}}\)
\( \newcommand\mib{\mathbf}\)
\( \newcommand\Sa{\textsf a}\)
\( \newcommand\Sb{\textsf b}\)
\( \newcommand\Sc{\textsf c}\)
\( \newcommand\Sd{\textsf d}\)
\( \newcommand\Se{\textsf e}\)
\( \newcommand\Sf{\textsf f}\)
\( \newcommand\Sg{\textsf g}\)
\( \newcommand\Sh{\textsf h}\)
\( \newcommand\Si{\textsf i}\)
\( \newcommand\Sj{\textsf j}\)
\( \newcommand\Sk{\textsf k}\)
\( \newcommand\Sl{\textsf l}\)
\( \newcommand\Sm{\textsf m}\)
\( \newcommand\Sn{\textsf n}\)
\( \newcommand\So{\textsf o}\)
\( \newcommand\Sp{\textsf p}\)
\( \newcommand\Sq{\textsf q}\)
\( \newcommand\Sr{\textsf r}\)
\( \newcommand\Ss{\textsf s}\)
\( \newcommand\St{\textsf t}\)
\( \newcommand\Su{\textsf u}\)
\( \newcommand\Sv{\textsf v}\)
\( \newcommand\Sw{\textsf w}\)
\( \newcommand\Sx{\textsf x}\)
\( \newcommand\Sy{\textsf y}\)
\( \newcommand\Sz{\textsf z}\)
\( \newcommand\SA{\textsf A}\)
\( \newcommand\SB{\textsf B}\)
\( \newcommand\SC{\textsf C}\)
\( \newcommand\SD{\textsf D}\)
\( \newcommand\SE{\textsf E}\)
\( \newcommand\SF{\textsf F}\)
\( \newcommand\SG{\textsf G}\)
\( \newcommand\SH{\textsf H}\)
\( \newcommand\SI{\textsf I}\)
\( \newcommand\SJ{\textsf J}\)
\( \newcommand\SK{\textsf K}\)
\( \newcommand\SL{\textsf L}\)
\( \newcommand\SM{\textsf M}\)
\( \newcommand\SN{\textsf N}\)
\( \newcommand\SO{\textsf O}\)
\( \newcommand\SP{\textsf P}\)
\( \newcommand\SQ{\textsf Q}\)
\( \newcommand\SR{\textsf R}\)
\( \newcommand\SS{\textsf S}\)
\( \newcommand\ST{\textsf T}\)
\( \newcommand\SU{\textsf U}\)
\( \newcommand\SV{\textsf V}\)
\( \newcommand\SW{\textsf W}\)
\( \newcommand\SX{\textsf X}\)
\( \newcommand\SY{\textsf Y}\)
\( \newcommand\SZ{\textsf Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Ha{\hat a}\)
\( \newcommand\Hb{\hat b}\)
\( \newcommand\Hc{\hat c}\)
\( \newcommand\Hd{\hat d}\)
\( \newcommand\He{\hat e}\)
\( \newcommand\Hf{\hat f}\)
\( \newcommand\Hg{\hat g}\)
\( \newcommand\Hh{\hat h}\)
\( \newcommand\Hi{\hat \imath}\)
\( \newcommand\Hj{\hat \jmath}\)
\( \newcommand\Hk{\hat k}\)
\( \newcommand\Hl{\hat l}\)
\( \newcommand\Hm{\hat m}\)
\( \newcommand\Hn{\hat n}\)
\( \newcommand\Ho{\hat o}\)
\( \newcommand\Hp{\hat p}\)
\( \newcommand\Hq{\hat q}\)
\( \newcommand\Hr{\hat r}\)
\( \newcommand\Hs{\hat s}\)
\( \newcommand\Ht{\hat t}\)
\( \newcommand\Hu{\hat u}\)
\( \newcommand\Hv{\hat v}\)
\( \newcommand\Hw{\hat w}\)
\( \newcommand\Hx{\hat x}\)
\( \newcommand\Hy{\hat y}\)
\( \newcommand\Hz{\hat z}\)
\( \newcommand\HA{\hat A}\)
\( \newcommand\HB{\hat B}\)
\( \newcommand\HC{\hat C}\)
\( \newcommand\HD{\hat D}\)
\( \newcommand\HE{\hat E}\)
\( \newcommand\HF{\hat F}\)
\( \newcommand\HG{\hat G}\)
\( \newcommand\HH{\hat H}\)
\( \newcommand\HI{\hat I}\)
\( \newcommand\HJ{\hat J}\)
\( \newcommand\HK{\hat K}\)
\( \newcommand\HL{\hat L}\)
\( \newcommand\HM{\hat M}\)
\( \newcommand\HN{\hat N}\)
\( \newcommand\HO{\hat O}\)
\( \newcommand\HP{\hat P}\)
\( \newcommand\HQ{\hat Q}\)
\( \newcommand\HR{\hat R}\)
\( \newcommand\HS{\hat S}\)
\( \newcommand\HT{\hat T}\)
\( \newcommand\HU{\hat U}\)
\( \newcommand\HV{\hat V}\)
\( \newcommand\HW{\hat W}\)
\( \newcommand\HX{\hat X}\)
\( \newcommand\HY{\hat Y}\)
\( \newcommand\HZ{\hat Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Halpha{\hat\alpha}\)
\( \newcommand\Hbeta{\hat\beta}\)
\( \newcommand\Hgamma{\hat\gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\Hdelta{\hat\delta}\)
\( \newcommand\Hepsilon{\hat\epsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvarepsilon{\hat\varepsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Hzeta{\hat\zeta}\)
\( \newcommand\Heta{\hat\eta}\)
\( \newcommand\Htheta{\hat\theta}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvartheta{\hat\vartheta}\)
\( \newcommand\Hiota{\hat\iota}\)
\( \newcommand\Hkappa{\hat\kappa}\)
\( \newcommand\Hlambda{\hat\lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\Hmu{\hat\mu}\)
\( \newcommand\Hnu{\hat\nu}\)
\( \newcommand\Hxi{\hat\xi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hom{\hat\omicron}\)
\( \newcommand\Hpi{\hat\pi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvarpi{\hat\varpi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hrho{\hat\rho}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvarrho{\hat\varrho}\)
\( \newcommand\Hsigma{\hat\sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvarsigma{\hat\varsigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Htau{\var\tau}\)
\( \newcommand\Hupsilon{\hat\upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Hphi{\hat\phi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hvarphi{\hat\varphi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hchi{\hat\chi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hxhi{\hat\xhi}\)
\( \newcommand\Hpsi{\hat\psi}\)
\( \newcommand\Homega{\hat\omega}\)
\( \newcommand\HGamma{\hat\Gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\HDelta{\hat\Delta}\)
\( \newcommand\HTheta{\hat\Theta}\)
\( \newcommand\HLambda{\hat\Lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\HXi{\hat\Xi}\)
\( \newcommand\HPi{\hat\Pi}\)
\( \newcommand\HSigma{\hat\Sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\HUps{\hat\Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\HPhi{\hat\Phi}\)
\( \newcommand\HPsi{\hat\Psi}\)
\( \newcommand\HOmega{\hat\Omega}\)
\( \newcommand\xhat{\hat\Bx}\)
\( \newcommand\yhat{\hat\By}\)
\( \newcommand\zhat{\hat\Bz}\)
\( \newcommand\ehat{\hat\Be}\)
\( \newcommand\khat{\hat\Bk}\)
\( \newcommand\nhat{\hat\Bn}\)
\( \newcommand\rhat{\hat\Br}\)
\( \newcommand\phihat{\hat\Bphi}\)
\( \newcommand\thetahat{\hat\Btheta}\)
\( \newcommand\MA{\mathbb A}\)
\( \newcommand\MB{\mathbb B}\)
\( \newcommand\MC{\mathbb C}\)
\( \newcommand\MD{\mathbb D}\)
\( \newcommand\ME{\mathbb E}\)
\( \newcommand\MF{\mathbb F}\)
\( \newcommand\MG{\mathbb G}\)
\( \newcommand\MH{\mathbb H}\)
\( \newcommand\MI{\mathbb I}\)
\( \newcommand\MJ{\mathbb J}\)
\( \newcommand\MK{\mathbb K}\)
\( \newcommand\ML{\mathbb L}\)
\( \newcommand\MM{\mathbb M}\)
\( \newcommand\MN{\mathbb N}\)
\( \newcommand\MO{\mathbb O}\)
\( \newcommand\MP{\mathbb P}\)
\( \newcommand\MQ{\mathbb Q}\)
\( \newcommand\MR{\mathbb R}\)
\( \newcommand\MS{\mathbb S}\)
\( \newcommand\MT{\mathbb T}\)
\( \newcommand\MU{\mathbb U}\)
\( \newcommand\MV{\mathbb V}\)
\( \newcommand\MW{\mathbb W}\)
\( \newcommand\MX{\mathbb X}\)
\( \newcommand\MY{\mathbb Y}\)
\( \newcommand\MZ{\mathbb Z}\)
\( \newcommand\CA{\mathcal A}\)
\( \newcommand\CB{\mathcal B}\)
\( \newcommand\CC{\mathcal C}\)
\( \newcommand\CD{\mathcal D}\)
\( \newcommand\CE{\mathcal E}\)
\( \newcommand\CF{\mathcal F}\)
\( \newcommand\CG{\mathcal G}\)
\( \newcommand\CH{\mathcal H}\)
\( \newcommand\CI{\mathcal I}\)
\( \newcommand\CJ{\mathcal J}\)
\( \newcommand\CK{\mathcal K}\)
\( \newcommand\CL{\mathcal L}\)
\( \newcommand\CM{\mathcal M}\)
\( \newcommand\CN{\mathcal N}\)
\( \newcommand\CO{\mathcal O}\)
\( \newcommand\CP{\mathcal P}\)
\( \newcommand\CQ{\mathcal Q}\)
\( \newcommand\CR{\mathcal R}\)
\( \newcommand\CS{\mathcal S}\)
\( \newcommand\CT{\mathcal T}\)
\( \newcommand\CU{\mathcal U}\)
\( \newcommand\CV{\mathcal V}\)
\( \newcommand\CW{\mathcal W}\)
\( \newcommand\CX{\mathcal X}\)
\( \newcommand\CY{\mathcal Y}\)
\( \newcommand\CZ{\mathcal Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Fa{\mathfrak a}\)
\( \newcommand\Fb{\mathfrak b}\)
\( \newcommand\Fc{\mathfrak c}\)
\( \newcommand\Fd{\mathfrak d}\)
\( \newcommand\Fe{\mathfrak e}\)
\( \newcommand\Ff{\mathfrak f}\)
\( \newcommand\Fg{\mathfrak g}\)
\( \newcommand\Fh{\mathfrak h}\)
\( \newcommand\Fi{\mathfrak i}\)
\( \newcommand\Fj{\mathfrak j}\)
\( \newcommand\Fk{\mathfrak k}\)
\( \newcommand\Fl{\mathfrak l}\)
\( \newcommand\Fm{\mathfrak m}\)
\( \newcommand\Fn{\mathfrak n}\)
\( \newcommand\Fo{\mathfrak o}\)
\( \newcommand\Fp{\mathfrak p}\)
\( \newcommand\Fq{\mathfrak q}\)
\( \newcommand\Fr{\mathfrak r}\)
\( \newcommand\Fs{\mathfrak s}\)
\( \newcommand\Ft{\mathfrak t}\)
\( \newcommand\Fu{\mathfrak u}\)
\( \newcommand\Fv{\mathfrak v}\)
\( \newcommand\Fw{\mathfrak w}\)
\( \newcommand\Fx{\mathfrak x}\)
\( \newcommand\Fy{\mathfrak y}\)
\( \newcommand\Fz{\mathfrak z}\)
\( \newcommand\FA{\mathfrak A}\)
\( \newcommand\FB{\mathfrak B}\)
\( \newcommand\FC{\mathfrak C}\)
\( \newcommand\FD{\mathfrak D}\)
\( \newcommand\FE{\mathfrak E}\)
\( \newcommand\FF{\mathfrak F}\)
\( \newcommand\FG{\mathfrak G}\)
\( \newcommand\FH{\mathfrak H}\)
\( \newcommand\FI{\mathfrak I}\)
\( \newcommand\FJ{\mathfrak J}\)
\( \newcommand\FK{\mathfrak K}\)
\( \newcommand\FL{\mathfrak L}\)
\( \newcommand\FM{\mathfrak M}\)
\( \newcommand\FN{\mathfrak N}\)
\( \newcommand\FO{\mathfrak O}\)
\( \newcommand\FP{\mathfrak P}\)
\( \newcommand\FQ{\mathfrak Q}\)
\( \newcommand\FR{\mathfrak R}\)
\( \newcommand\FS{\mathfrak S}\)
\( \newcommand\FT{\mathfrak T}\)
\( \newcommand\FU{\mathfrak U}\)
\( \newcommand\FV{\mathfrak V}\)
\( \newcommand\FW{\mathfrak W}\)
\( \newcommand\FX{\mathfrak X}\)
\( \newcommand\FY{\mathfrak Y}\)
\( \newcommand\FZ{\mathfrak Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Da{\dot a}\)
\( \newcommand\Db{\dot b}\)
\( \newcommand\Dc{\dot c}\)
\( \newcommand\Dd{\dot d}\)
\( \newcommand\De{\dot e}\)
\( \newcommand\Df{\dot f}\)
\( \newcommand\Dg{\dot g}\)
\( \newcommand\Dh{\dot h}\)
\( \newcommand\Di{\dot \imath}\)
\( \newcommand\Dj{\dot \jmath}\)
\( \newcommand\Dk{\dot k}\)
\( \newcommand\Dl{\dot l}\)
\( \newcommand\Dm{\dot m}\)
\( \newcommand\Dn{\dot n}\)
\( \newcommand\Do{\dot o}\)
\( \newcommand\Dp{\dot p}\)
\( \newcommand\Dq{\dot q}\)
\( \newcommand\Dr{\dot r}\)
\( \newcommand\Ds{\dot s}\)
\( \newcommand\Dt{\dot t}\)
\( \newcommand\Du{\dot u}\)
\( \newcommand\Dv{\dot v}\)
\( \newcommand\Dw{\dot w}\)
\( \newcommand\Dx{\dot x}\)
\( \newcommand\Dy{\dot y}\)
\( \newcommand\Dz{\dot z}\)
\( \newcommand\DA{\dot A}\)
\( \newcommand\DB{\dot B}\)
\( \newcommand\DC{\dot C}\)
\( \newcommand\DD{\dot D}\)
\( \newcommand\DE{\dot E}\)
\( \newcommand\DF{\dot F}\)
\( \newcommand\DG{\dot G}\)
\( \newcommand\DH{\dot H}\)
\( \newcommand\DI{\dot I}\)
\( \newcommand\DJ{\dot J}\)
\( \newcommand\DK{\dot K}\)
\( \newcommand\DL{\dot L}\)
\( \newcommand\DM{\dot M}\)
\( \newcommand\DN{\dot N}\)
\( \newcommand\DO{\dot O}\)
\( \newcommand\DP{\dot P}\)
\( \newcommand\DQ{\dot Q}\)
\( \newcommand\DR{\dot R}\)
\( \newcommand\DS{\dot S}\)
\( \newcommand\DT{\dot T}\)
\( \newcommand\DU{\dot U}\)
\( \newcommand\DV{\dot V}\)
\( \newcommand\DW{\dot W}\)
\( \newcommand\DX{\dot X}\)
\( \newcommand\DY{\dot Y}\)
\( \newcommand\DZ{\dot Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Dalpha
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[1], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dbeta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[2], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dgamma
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[3], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Ddelta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[4], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Depsilon
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[5], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dvarepsilon
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[6], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dzeta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[7], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Deta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[8], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dtheta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[9], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dvartheta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[10], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Diota
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[11], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dkappa
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[12], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dlambda
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[13], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Dmu{\dot\mu}\)
\( \newcommand\Dnu{\dot\nu}\)
\( \newcommand\Dxi{\dot\xi}\)
\( \newcommand\Dom{\dot\omicron}\)
\( \newcommand\Dpi{\dot\pi}\)
\( \newcommand\Dvarpi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[14], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Drho{\dot\rho}\)
\( \newcommand\Dvarrho{\dot\varrho}\)
\( \newcommand\Dsigma{\dot\sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Dvarsigma{\dot\varsigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Dtau{\var\tau}\)
\( \newcommand\Dupsilon{\dot\upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Dphi{\dot\phi}\)
\( \newcommand\Dvarphi{\dot\varphi}\)
\( \newcommand\Dchi{\dot\chi}\)
\( \newcommand\Dpsi{\dot\psi}\)
\( \newcommand\Domega{\dot\omega}\)
\( \newcommand\DGamma
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[15], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\DDelta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[16], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\DTheta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[17], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\DLambda{\dot\Lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\DXi{\dot\Xi}\)
\( \newcommand\DPi{\dot\Pi}\)
\( \newcommand\DSigma{\dot\Sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\DUps{\dot\Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\DPhi{\dot\Phi}\)
\( \newcommand\DPsi{\dot\Psi}\)
\( \newcommand\DOmega{\dot\Omega}\)
\( \newcommand\Va{\vec a}\)
\( \newcommand\Vb{\vec b}\)
\( \newcommand\Vc{\vec c}\)
\( \newcommand\Vd{\vec d}\)
\( \newcommand\Ve{\vec e}\)
\( \newcommand\Vf{\vec f}\)
\( \newcommand\Vg{\vec g}\)
\( \newcommand\Vh{\vec h}\)
\( \newcommand\Vi{\vec \imath}\)
\( \newcommand\Vj{\vec \jmath}\)
\( \newcommand\Vk{\vec k}\)
\( \newcommand\Vl{\vec l}\)
\( \newcommand\Vm{\vec m}\)
\( \newcommand\Vn{\vec n}\)
\( \newcommand\Vo{\vec o}\)
\( \newcommand\Vp{\vec p}\)
\( \newcommand\Vq{\vec q}\)
\( \newcommand\Vr{\vec r}\)
\( \newcommand\Vs{\vec s}\)
\( \newcommand\Vt{\vec t}\)
\( \newcommand\Vu{\vec u}\)
\( \newcommand\Vv{\vec v}\)
\( \newcommand\Vw{\vec w}\)
\( \newcommand\Vx{\vec x}\)
\( \newcommand\Vy{\vec y}\)
\( \newcommand\Vz{\vec z}\)
\( \newcommand\VA{\vec A}\)
\( \newcommand\VB{\vec B}\)
\( \newcommand\VC{\vec C}\)
\( \newcommand\VD{\vec D}\)
\( \newcommand\VE{\vec E}\)
\( \newcommand\VF{\vec F}\)
\( \newcommand\VG{\vec G}\)
\( \newcommand\VH{\vec H}\)
\( \newcommand\VI{\vec I}\)
\( \newcommand\VJ{\vec J}\)
\( \newcommand\VK{\vec K}\)
\( \newcommand\VL{\vec L}\)
\( \newcommand\VM{\vec M}\)
\( \newcommand\VN{\vec N}\)
\( \newcommand\VO{\vec O}\)
\( \newcommand\VP{\vec P}\)
\( \newcommand\VQ{\vec Q}\)
\( \newcommand\VR{\vec R}\)
\( \newcommand\VS{\vec S}\)
\( \newcommand\VT{\vec T}\)
\( \newcommand\VU{\vec U}\)
\( \newcommand\VV{\vec V}\)
\( \newcommand\VW{\vec W}\)
\( \newcommand\VX{\vec X}\)
\( \newcommand\VY{\vec Y}\)
\( \newcommand\VZ{\vec Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Valpha{\vec\alpha}\)
\( \newcommand\Vbeta{\vec\beta}\)
\( \newcommand\Vgamma{\vec\gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\Vdelta{\vec\delta}\)
\( \newcommand\Vepsilon{\vec\epsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Vvarepsilon{\vec\varepsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Vzeta{\vec\zeta}\)
\( \newcommand\Veta{\vec\eta}\)
\( \newcommand\Vtheta{\vec\theta}\)
\( \newcommand\Vvartheta{\vec\vartheta}\)
\( \newcommand\Viota{\vec\iota}\)
\( \newcommand\Vkappa{\vec\kappa}\)
\( \newcommand\Vlambda{\vec\lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\Vmu
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[18], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vnu
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[19], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vxi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[20], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vom
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[21], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vpi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[22], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vvarpi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[23], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vrho
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[24], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vvarrho
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[25], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vsigma
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[26], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vvarsigma
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[27], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vtau
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[28], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vupsilon
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[29], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vphi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[30], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vvarphi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[31], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vchi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[32], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vpsi
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[33], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\Vomega
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[34], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\VGamma
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[35], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\VDelta
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/p[1]/span[36], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\VTheta{\vec\Theta}\)
\( \newcommand\VLambda{\vec\Lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\VXi{\vec\Xi}\)
\( \newcommand\VPi{\vec\Pi}\)
\( \newcommand\VSigma{\vec\Sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\VUps{\vec\Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\VPhi{\vec\Phi}\)
\( \newcommand\VPsi{\vec\Psi}\)
\( \newcommand\VOmega{\vec\Omega}\)
\( \newcommand\BA{\mib A}\)
\( \newcommand\BB{\mib B}\)
\( \newcommand\BC{\mib C}\)
\( \newcommand\BD{\mib D}\)
\( \newcommand\BE{\mib E}\)
\( \newcommand\BF{\mib F}\)
\( \newcommand\BG{\mib G}\)
\( \newcommand\BH{\mib H}\)
\( \newcommand\BI{\mib I}}\)
\( \newcommand\BJ{\mib J}\)
\( \newcommand\BK{\mib K}\)
\( \newcommand\BL{\mib L}\)
\( \newcommand\BM{\mib M}\)
\( \newcommand\BN{\mib N}\)
\( \newcommand\BO{\mib O}\)
\( \newcommand\BP{\mib P}\)
\( \newcommand\BQ{\mib Q}\)
\( \newcommand\BR{\mib R}\)
\( \newcommand\BS{\mib S}\)
\( \newcommand\BT{\mib T}\)
\( \newcommand\BU{\mib U}\)
\( \newcommand\BV{\mib V}\)
\( \newcommand\BW{\mib W}\)
\( \newcommand\BX{\mib X}\)
\( \newcommand\BY{\mib Y}\)
\( \newcommand\BZ{\mib Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Ba{\mib a}\)
\( \newcommand\Bb{\mib b}\)
\( \newcommand\Bc{\mib c}\)
\( \newcommand\Bd{\mib d}\)
\( \newcommand\Be{\mib e}\)
\( \newcommand\Bf{\mib f}\)
\( \newcommand\Bg{\mib g}\)
\( \newcommand\Bh{\mib h}\)
\( \newcommand\Bi{\mib i}\)
\( \newcommand\Bj{\mib j}\)
\( \newcommand\Bk{\mib k}\)
\( \newcommand\Bl{\mib l}\)
\( \newcommand\Bm{\mib m}\)
\( \newcommand\Bn{\mib n}\)
\( \newcommand\Bo{\mib o}\)
\( \newcommand\Bp{\mib p}\)
\( \newcommand\Bq{\mib q}\)
\( \newcommand\Br{\mib r}\)
\( \newcommand\Bs{\mib s}\)
\( \newcommand\Bt{\mib t}\)
\( \newcommand\Bu{\mib u}\)
\( \newcommand\Bv{\mib v}\)
\( \newcommand\Bw{\mib w}\)
\( \newcommand\Bx{\mib x}\)
\( \newcommand\By{\mib y}\)
\( \newcommand\Bz{\mib z}\)\)
\( \newcommand\vrh{\varrho}\)
\( \newcommand\vsig{\varsigma}\)
\( \newcommand\ups{\upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\eps{\epsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\ve{\varepsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\vth{\vartheta}\)
\( \newcommand\vphi{\varphi}\)
\( \newcommand\xhi{\chi}\)
\( \newcommand\Ups{\Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Balpha{\mib\alpha}\)
\( \newcommand\Bbeta{\mib\beta}\)
\( \newcommand\Bgamma{\mib\gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\Bdelta{\mib\delta}\)
\( \newcommand\Beps{\mib\epsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Bve{\mib\varepsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Bzeta{\mib\zeta}\)
\( \newcommand\Beta{\mib\eta}\)
\( \newcommand\Btheta{\mib\theta}\)
\( \newcommand\Bvth{\mib\vartheta}\)
\( \newcommand\Biota{\mib\iota}\)
\( \newcommand\Bkappa{\mib\kappa}\)
\( \newcommand\Blambda{\mib\lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\Bmu{\mib\mu}\)
\( \newcommand\Bnu{\mib\nu}\)
\( \newcommand\Bxi{\mib\xi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bom{\mib\omicron}\)
\( \newcommand\Bpi{\mib\pi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bvarpi{\mib\varpi}\)
\( \newcommand\Brho{\mib\rho}\)
\( \newcommand\Bvrh{\mib\varrho}\)
\( \newcommand\Bsigma{\mib\sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Bvsig{\mib\varsigma}\)
\( \newcommand\Btau{\mib\tau}\)
\( \newcommand\Bups{\mib\upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\Bphi{\mib\phi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bvphi{\mib\vphi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bchi{\mib\chi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bpsi{\mib\psi}\)
\( \newcommand\Bomega{\mib\omega}\)
\( \newcommand\BGamma{\mib\Gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\BDelta{\mib\Delta}\)
\( \newcommand\BTheta{\mib\Theta}\)
\( \newcommand\BLambda{\mib\Lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\BXi{\mib\Xi}\)
\( \newcommand\BPi{\mib\Pi}\)
\( \newcommand\BSigma{\mib\Sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\BUps{\mib\Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\BPhi{\mib\Phi}\)
\( \newcommand\BPsi{\mib\Psi}\)
\( \newcommand\BOmega{\mib\Omega}\)
\( \newcommand\Bxhi{\raise.35ex\hbox{$\Bchi$}}\)
\( \newcommand\RGamma{ \Gamma}\)
\( \newcommand\RDelta{ \Delta}\)
\( \newcommand\RTheta{ \Theta}\)
\( \newcommand\RLambda{ \Lambda}\)
\( \newcommand\RXi{ \Xi}\)
\( \newcommand\RPi{ \Pi}\)
\( \newcommand\RSigma{ \Sigma}\)
\( \newcommand\RUps{ \Upsilon}\)
\( \newcommand\RPhi{ \Phi}\)
\( \newcommand\RPsi{ \Psi}\)
\( \newcommand\ROmega{ \Omega}\)
\( \newcommand\RA{ A}\)
\( \newcommand\RB{ B}\)
\( \newcommand\RC{ C}\)
\( \newcommand\RD{ D}\)
\( \newcommand\RE{ E}\)
\( \newcommand\RF{ F}\)
\( \newcommand\RG{ G}\)
\( \newcommand\RH{ H}\)
\( \newcommand\RI{ I}\)
\( \newcommand\RJ{ J}\)
\( \newcommand\RK{ K}\)
\( \newcommand\RL{ L}\)
\( \newcommand { M}\)
\( \newcommand\RN{ N}\)
\( \newcommand\RO{ O}\)
\( \newcommand\RP{ P}\)
\( \newcommand\RQ{ Q}\)
\( \newcommand\RR{ R}\)
\( \newcommand\RS{ S}\)
\( \newcommand\RT{ T}\)
\( \newcommand\RU{ U}\)
\( \newcommand\RV{ V}\)
\( \newcommand\RW{ W}\)
\( \newcommand\RX{ X}\)
\( \newcommand\RY{ Y}\)
\( \newcommand\RZ{ Z}\)
\( \newcommand\Ra{ a}\)
\( \newcommand\Rb{ b}\)
\( \newcommand\Rc{ c}\)
\( \newcommand\Rd{ d}\)
\( \newcommand\Re{ e}\)
\( \newcommand\Rf{ f}\)
\( \newcommand\Rg{ g}\)
\( \newcommand\Rh{ h}\)
\( \newcommand\Ri{ i}\)
\( \newcommand\Rj{ j}\)
\( \newcommand\Rk{ k}\)
\( \newcommand\Rl{ l}\)
\( \newcommand { m}\)
\( \newcommand\Rn{ n}\)
\( \newcommand\Ro{ o}\)
\( \newcommand\Rp{ p}\)
\( \newcommand\Rq{ q}\)
\( \newcommand\Rr{ r}\)
\( \newcommand\Rs{ s}\)
\( \newcommand\Rt{ t}\)
\( \newcommand\Ru{ u}\)
\( \newcommand\Rv{ v}\)
\( \newcommand\Rw{ w}\)
\( \newcommand\Rx{ x}\)
\( \newcommand\Ry{ y}\)
\( \newcommand\Rz{ z}\)
\( \newcommand\BBA{\boldsymbol\RA}\)
\( \newcommand\BBB{\boldsymbol\RB}\)
\( \newcommand\BBC{\boldsymbol\RC}\)
\( \newcommand\BBD{\boldsymbol\RD}\)
\( \newcommand\BBE{\boldsymbol\RE}\)
\( \newcommand\BBF{\boldsymbol\RF}\)
\( \newcommand\BBG{\boldsymbol\RG}\)
\( \newcommand\BBH{\boldsymbol\RH}\)
\( \newcommand\BBI{\boldsymbol\RI}\)
\( \newcommand\BBJ{\boldsymbol\RJ}\)
\( \newcommand\BBK{\boldsymbol\RK}\)
\( \newcommand\BBL{\boldsymbol\RL}\)
\( \newcommand\BBM{\boldsymbol }\)
\( \newcommand\BBN{\boldsymbol\RN}\)
\( \newcommand\BBO{\boldsymbol\RO}\)
\( \newcommand\BBP{\boldsymbol\RP}\)
\( \newcommand\BBQ{\boldsymbol\RQ}\)
\( \newcommand\BBR{\boldsymbol\RR}\)
\( \newcommand\BBS{\boldsymbol\RS}\)
\( \newcommand\BBT{\boldsymbol\RT}\)
\( \newcommand\BBU{\boldsymbol\RU}\)
\( \newcommand\BBV{\boldsymbol\RV}\)
\( \newcommand\BBW{\boldsymbol\RW}\)
\( \newcommand\BBX{\boldsymbol\RX}\)
\( \newcommand\BBY{\boldsymbol\RY}\)
\( \newcommand\BBZ{\boldsymbol\RZ}\)
\( \newcommand\BBa{\boldsymbol\Ra}\)
\( \newcommand\BBb{\boldsymbol\Rb}\)
\( \newcommand\BBc{\boldsymbol\Rc}\)
\( \newcommand\BBd{\boldsymbol\Rd}\)
\( \newcommand\BBe{\boldsymbol\Re}\)
\( \newcommand\BBf{\boldsymbol\Rf}\)
\( \newcommand\BBg{\boldsymbol\Rg}\)
\( \newcommand\BBh{\boldsymbol\Rh}\}\)
\( \newcommand\BBi{\boldsymbol\Ri}\)
\( \newcommand\BBj{\boldsymbol\Rj}\)
\( \newcommand\BBk{\boldsymbol\Rk}\)
\( \newcommand\BBl{boldsymbol\Rl}\)
\( \newcommand\BBm{\boldsymbol }\)
\( \newcommand\BBn{\boldsymbol\Rn}\)
\( \newcommand\BBo{\boldsymbol\Ro}\)
\( \newcommand\BBp{\boldsymbol\Rp}\)
\( \newcommand\BBq{\boldsymbol\Rq}\)
\( \newcommand\BBr{\boldsymbol\Rr}\)
\( \newcommand\BBs{\boldsymbol\Rs}\)
\( \newcommand\BBt{\boldsymbol\Rt}\)
\( \newcommand\BBu{\boldsymbol\Ru}\)
\( \newcommand\BBv{\boldsymbol\Rv}\)
\( \newcommand\BBw{\boldsymbol\Rw}\)
\( \newcommand\BBx{\boldsymbol\Rx}\)
\( \newcommand\BBy{\boldsymbol\Ry}\)
\( \newcommand\BBz{\boldsymbol\Rz}\)
\( \newcommand\tcb{\textcolor{blue}\)
\( \newcommand\tcr{\textcolor{red}\)
\( \newcommand\bnabla{\boldsymbol{\nabla}}\)
\( \newcommand\Bell{\boldsymbol\ell}\)
\( \newcommand\dbar{\,{\mathchar'26\mkern-12mu d}} \)
\( \newcommand\ns{^\vphantom{*}}\)
\( \newcommand\uar{\uparrow}\)
\( \newcommand\dar{\downarrow}\)
\( \newcommand\impi{\int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty}\!\!}\)
\( \newcommand\izpi{\int\limits_{0}^{\infty}\!\!}\)
\( \newcommand\etc{\it etc.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\etal{\it et al.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\opcit{\it op. cit.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\ie{\it i.e.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\Ie{\it I.e.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\viz{\it viz.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\eg{\it e.g.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\Eg{\it E.g.\/}\)
\( \newcommand\dbar{\,{\mathchar'26\mkern-12mu d}} \)
\( \def\sss#1{\scriptscriptstyle #1}\)
\( \def\ss#1{\scriptstyle #1}\)
\( \def\ssr#1{\scriptstyle #1}\)
\( \def\ssf#1{\scriptstyle #1}\)
\( \newcommand\NA{N_{\ssr{\!A}}}\)
\( \newcommand\lala{\langle\!\langle}\)
\( \newcommand\rara{\rangle\!\rangle}\)
\( \newcommand\blan{\big\langle}\)
\( \newcommand\bran{\big\rangle}\)
\( \newcommand\Blan{\Big\langle}\)
\( \newcommand\Bran{\Big\rangle}\)
\( \newcommand\intl{\int\limits}\)
\( \newcommand\half{\frac{1}{2}}\)
\( \newcommand\third{\frac{1}{3}}\)
\( \newcommand\fourth{\frac{1}{4}}\)
\( \newcommand\eighth{\frac{1}{8}}\)
\( \newcommand\uar{\uparrow}\)
\( \newcommand\dar{\downarrow}\)
\( \newcommand\undertext#1{$\underline{\hbox{#1}}$}\)
\( \newcommand\Tra{\mathop{\textsf{Tr}}\,}\)
\( \newcommand\det{\mathop{\textsf{det}}\,}\)
\( \def\tket#1{| #1 \rangle}\)
\( \def\tbra#1{\langle #1|}\)
\( \def\tbraket#1#2{\langle #1 | #2 \rangle}\)
\( \def\texpect#1#2#3{\langle #1 | #2 | #3 \rangle}\)
\( \def\sket#1{| \, #1 \, \rangle}\)
\( \def\sbra#1{\langle \, #1 \, |}\)
\( \def\sbraket#1#2{\langle \, #1 \, | \, #2 \, \rangle}\)
\( \def\sexpect#1#2#3{\langle \, #1 \, | \, #2 \, | \, #3 \, \rangle}\)
\(\def\ket#1{\big| \, #1\, \big\rangle}\)
\( \def\bra#1{\big\langle \, #1 \, \big|}\)
\( \def\braket#1#2{\big\langle \, #1\, \big| \,#2 \,\big\rangle}\)
\( \def\expect#1#2#3{\big\langle\, #1\, \big|\, #2\, \big| \,#3\, \big\rangle}\)
\( \newcommand\pz{\partial}\)
\( \newcommand\pzb{\bar{\partial}}\)
\( \newcommand\svph{\vphantom{\int}}\)
\( \newcommand\vph{\vphantom{\sum_i}}\)
\( \newcommand\bvph{\vphantom{\sum_N^N}}\)
\( \newcommand\nd{^{\vphantom{\dagger}}}\)
\( \newcommand\ns{^{\vphantom{*}}}\)
\( \newcommand\yd{^\dagger}\)
\( \newcommand\zb{\bar z}\)
\( \newcommand\zdot{\dot z}\)
\( \newcommand\zbdot{\dot{\bar z}}\)
\( \newcommand\kB{k_{\sss{B}}}\)
\( \newcommand\kT{k_{\sss{B}}T}\)
\( \newcommand\gtau{g_\tau}\)
\( \newcommand\Htil{\tilde H}\)
\( \newcommand\pairo{(\phi\nd_0,J\nd_0)}\)
\( \newcommand\pairm{(\phi\nd_0,J)}\)
\( \newcommand\pairob{(\Bphi\nd_0,\BJ\nd_0)}\)
\( \newcommand\pairmb{(\Bphi\nd_0,\BJ)}\)
\( \newcommand\pair{(\phi,J)}\)
\( \newcommand\Hz{H\nd_0}\)
\( \newcommand\Ho{H\nd_1}\)
\( \newcommand\Htz{\Htil\nd_0}\)
\( \newcommand\Hto{\Htil\nd_1}\)
\( \newcommand\oc{\omega_\Rc}\)
\(\newcommand \gtwid{\approx}\)
\( \newcommand\index{\textsf{ind}}\)
\( \newcommand\csch{\,{ csch\,}}\)
\( \newcommand\ctnh{\,{ ctnh\,}}\)
\( \newcommand\ctn{\,{ ctn\,}}\)
\( \newcommand\sgn{\,{ sgn\,}}\)
\( \def\tmapright#1{\xrightarrow \limits^{#1}}\)
\( \def\bmapright#1{\xrightarrow\limits_{#1}}\)
\( \newcommand\hfb{\hfill\break}\)
\( \newcommand\Rep{\textsf{Re}\,}\)
\( \newcommand\Imp{\textsf{Im}\,}\)
\( \newcommand\ncdot{\!\cdot\!}\)
\( \def\tmapright#1{ \smash{\mathop{\hbox to 35pt{\rightarrowfill}}\limits^{#1}}\ }\)
\( \def\bmapright#1{ \smash{\mathop{\hbox to 35pt{\rightarrowfill}}\limits_{#1}}\ }\)
\( \newcommand\bsqcap{\mbox{\boldmath{$\sqcap$}}}\)
\( \def\spabc#1#2#3{\big({\pz #1\over\pz #2}\big)\ns_{\!#3}}\)
\( \def\qabc#1#2#3{\pz^2\! #1\over\pz #2\,\pz #3}\)
\( \def\rabc#1#2#3#4{(\pz #1,\pz #2)\over (\pz #3,\pz #4)}\)
\( \newcommand\subA{\ns_\ssr{A}}\)
\( \newcommand\subB{\ns_\ssr{B}}\)
\( \newcommand\subC{\ns_\ssr{C}}\)
\( \newcommand\subD{\ns_\ssr{D}}\)
\( \newcommand\subAB{\ns_\ssr{AB}}\)
\( \newcommand\subBC{\ns_\ssr{BC}}\)
\( \newcommand\subCD{\ns_\ssr{CD}}\)
\( \newcommand\subDA{\ns_\ssr{DA}}\)
\( \def\lmapright#1{\ \ \smash{\mathop{\hbox to 55pt{\rightarrowfill}}\limits^{#1}}\ \ }\)
\( \def\enth#1{\RDelta {\textsf H}^0_\Rf[{ #1}]}\)
\( \newcommand\longrightleftharpoons{ \mathop{\vcenter{\hbox{\ooalign{\raise1pt\hbox{$\longrightharpoonup\joinrel$}\crcr \lower1pt\hbox{$\longleftharpoondown\joinrel$}}}}}}\)
\( \newcommand\longrightharpoonup{\relbar\joinrel\rightharpoonup}\)
\( \newcommand\longleftharpoondown{\leftharpoondown\joinrel\relbar}\)
\( \newcommand\cds{\,\bullet\,}\)
\( \newcommand\ccs{\,\circ\,}\)
\( \newcommand\nsub{_{\vphantom{\dagger}}}\)
\( \newcommand\rhohat{\hat\rho}\)
\( \newcommand\vrhhat{\hat\vrh}\)
\( \newcommand\impi{\int\limits_{-\infty}^\infty\!\!\!}\)
\( \newcommand\brangle{\big\rangle}\)
\( \newcommand\blangle{\big\langle}\)
\( \newcommand\vet{\tilde\ve}\)
\( \newcommand\zbar{\bar z}\)
\( \newcommand\ftil{\tilde f}\)
\( \newcommand\XBE{\RXi\ns_\ssr{BE}}\)
\( \newcommand\XFD{\RXi\ns_\ssr{FD}}\)
\( \newcommand\OBE{\Omega\ns_\ssr{BE}}\)
\( \newcommand\OFD{\Omega\ns_\ssr{FD}}\)
\( \newcommand\veF{\ve\ns_\RF}\)
\( \newcommand\kF{k\ns_\RF}\)
\( \newcommand\kFu{k\ns_{\RF\uar}}\)
\( \newcommand\SZ{\textsf Z}}\) \( \newcommand\kFd{k\ns_{\RF\dar}\)
\( \newcommand\muB{\mu\ns_\ssr{B}}\)
\( \newcommand\mutB{\tilde\mu}\ns_\ssr{B}\)
\( \newcommand\xoN{\Bx\ns_1\,,\,\ldots\,,\,\Bx\ns_N}\)
\( \newcommand\rok{\Br\ns_1\,,\,\ldots\,,\,\Br\ns_k}\)
\( \newcommand\xhiOZ{\xhi^\ssr{OZ}}\)
\( \newcommand\xhihOZ
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/span[1], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\jhz{\HJ(0)}\)
\( \newcommand\nda{\nd_\alpha}\)
\( \newcommand\ndap{\nd_{\alpha'}}\)
\( \newcommand\labar
Callstack:
at (Template:MathJaxArovas), /content/body/div/span[2], line 1, column 1
at template()
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/p[1]/span, line 1, column 23
\( \newcommand\msa{m\ns_\ssr{A}}\)
\( \newcommand\msb{m\ns_\ssr{B}}\)
\( \newcommand\mss{m\ns_\Rs}\)
\( \newcommand\HBx{\hat\Bx}\)
\( \newcommand\HBy{\hat\By}\)
\( \newcommand\HBz{\hat\Bz}\)
\( \newcommand\thm{\theta\ns_m}\)
\( \newcommand\thp{\theta\ns_\phi}\)
\( \newcommand\mtil{\widetilde m}\)
\( \newcommand\phitil{\widetilde\phi}\)
\( \newcommand\delf{\delta\! f}\)
\( \newcommand\coll{\bigg({\pz f\over\pz t}\bigg)\nd_{\! coll}}\)
\( \newcommand\stre{\bigg({\pz f\over\pz t}\bigg)\nd_{\! str}}\)
\( \newcommand\idrp{\int\!\!{d^3\!r\,d^3\!p\over h^3}\>}\)
\( \newcommand\vbar{\bar v}\)
\( \newcommand\BCE{\mbox{\boldmath{$\CE$}}\!}\)
\( \newcommand\BCR{\mbox{\boldmath{$\CR$}}\!}\)
\( \newcommand\gla{g\nd_{\RLambda\nd}}\)
\( \newcommand\TA{T\ns_\ssr{A}}\)
\( \newcommand\TB{T\ns_\ssr{B}}\)
\( \newcommand\ncdot{\!\cdot\!}\)
\( \newcommand\NS{N\ns_{\textsf S}}\)
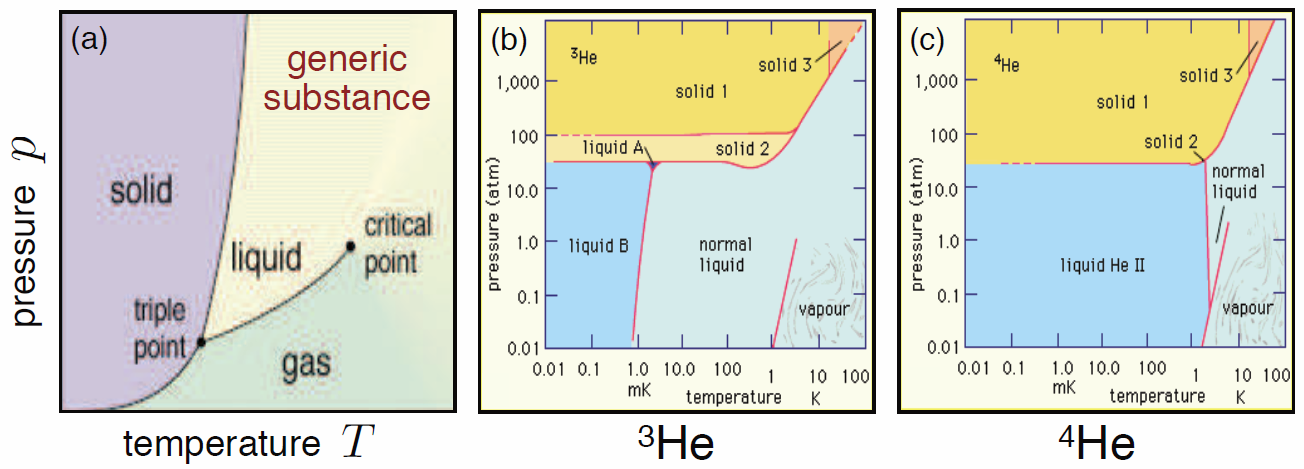
A typical phase diagram of a \(p\)-\(V\)-\(T\) system is shown in the Fig. [pdiaga](a). The solid lines delineate boundaries between distinct thermodynamic phases. These lines are called coexistence curves. Along these curves, we can have coexistence of two phases, and the thermodynamic potentials are singular. The order of the singularity is often taken as a classification of the phase transition. if the thermodynamic potentials \(E\), \(F\), \(G\), and \(\CH\) have discontinuous or divergent \(m^\ssr{th}\) derivatives, the transition between the respective phases is said to be \(m^\ssr{th}\) order. Modern theories of phase transitions generally only recognize two possibilities: first order transitions, where the order parameter changes discontinuously through the transition, and second order transitions, where the order parameter vanishes continuously at the boundary from ordered to disordered phases12. We’ll discuss order parameters during Physics 140B.
For a more interesting phase diagram, see Fig. [pdiaga](b,c), which displays the phase diagrams for \({}^3\)He and \({}^4\)He. The only difference between these two atoms is that the former has one fewer neutron: (2p + 1n + 2e) in \({}^3\)He versus (2p + 2n + 2e) in \({}^4\)He. As we shall learn when we study quantum statistics, this extra neutron makes all the difference, because \({}^3\)He is a fermion while \({}^4\)He is a boson.
\(p\)-\(v\)-\(T\) surfaces
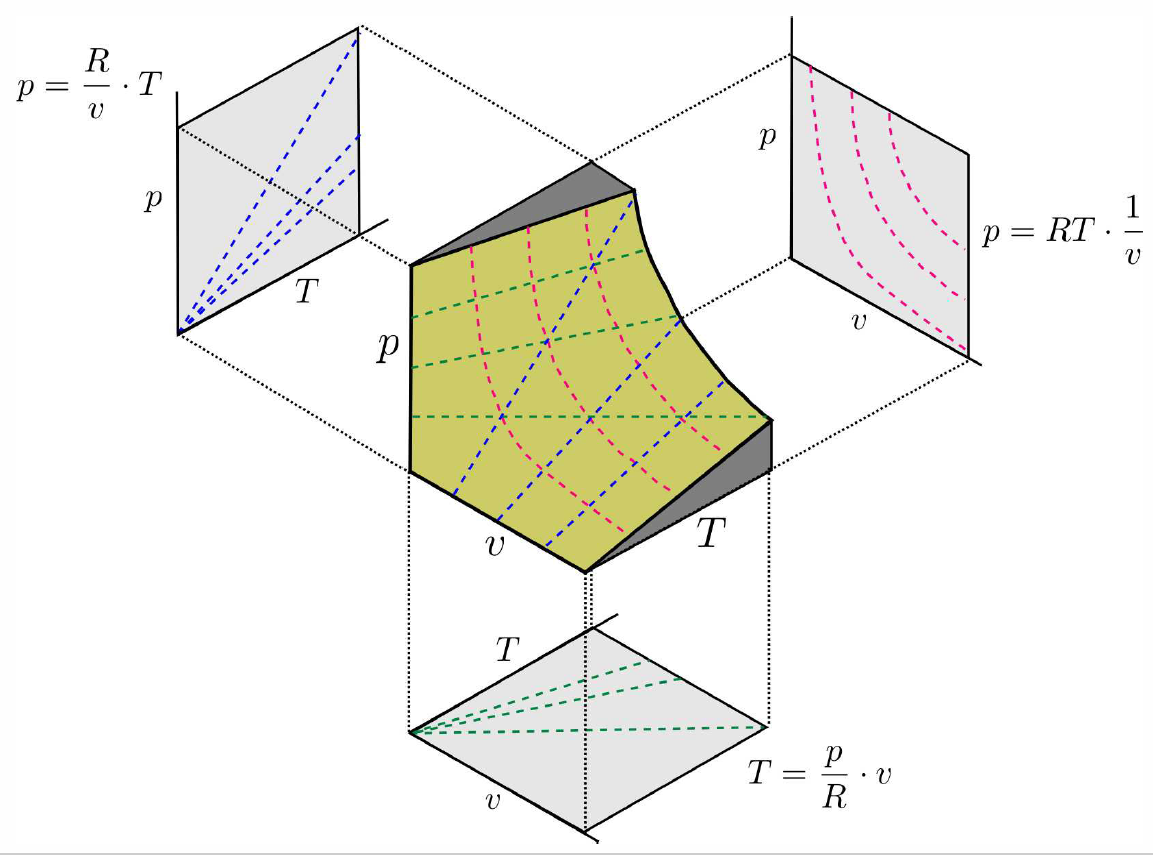
The equation of state for a single component system may be written as \[f(p,v,T)=0\ .\] This may in principle be inverted to yield \(p=p(v,T)\) or \(v=v(T,p)\) or \(T=T(p,v)\). The single constraint \(f(p,v,T)\) on the three state variables defines a surface in \(\{p,v,T\}\) space. An example of such a surface is shown in Fig. [PVTideal], for the ideal gas.
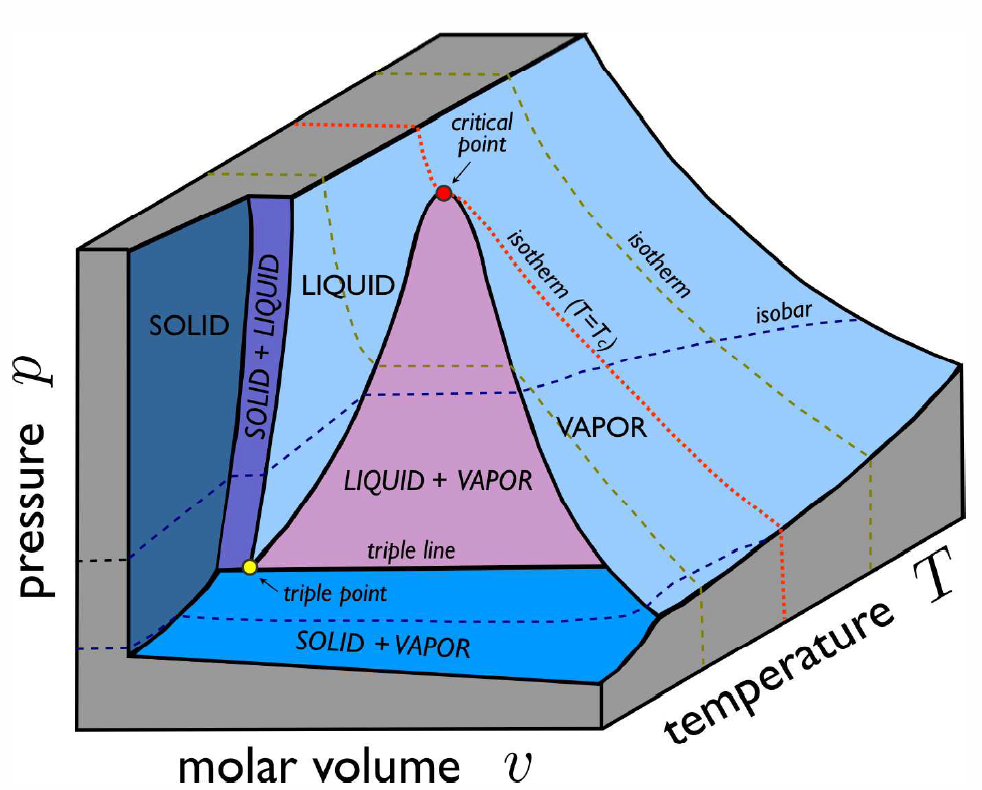
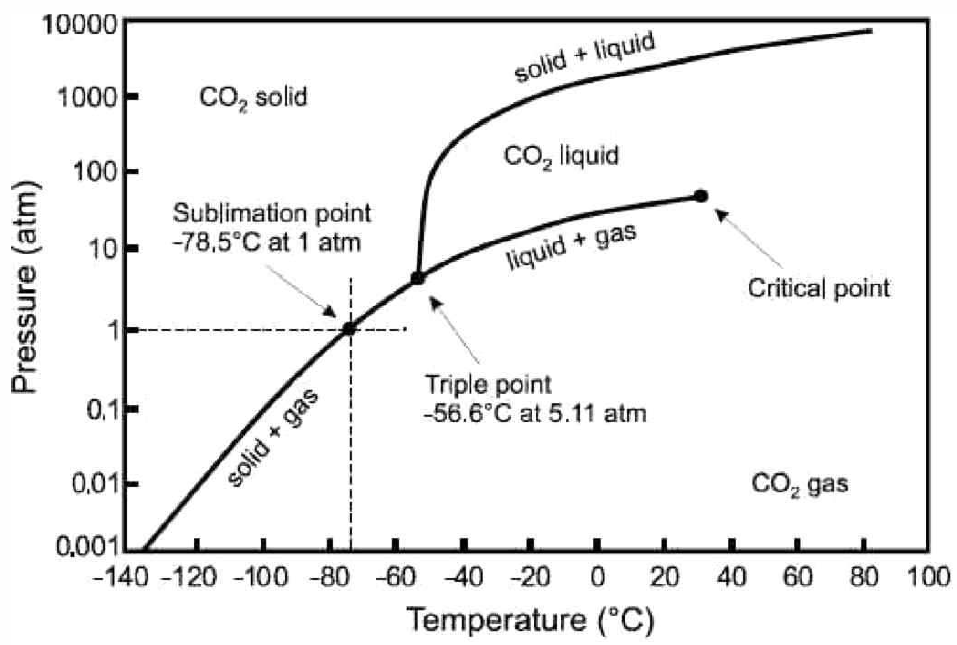
Real \(p\)-\(v\)-\(T\) surfaces are much richer than that for the ideal gas, because real systems undergo phase transitions in which thermodynamic properties are singular or discontinuous along certain curves on the \(p\)-\(v\)-\(T\) surface. An example is shown in Fig. [PVTa]. The high temperature isotherms resemble those of the ideal gas, but as one cools below the critical temperature \(T\ns_\Rc\), the isotherms become singular. Precisely at \(T=T\ns_\Rc\), the isotherm \(p=p(v,T\ns_\Rc)\) becomes perfectly horizontal at \(v=v\ns_\Rc\), which is the critical molar volume. This means that the isothermal compressibility, \(\kappa\ns_T=-{1\over v}\big({\pz v\over\pz p}\big)\nd_T\) diverges at \(T=T\ns_\Rc\). Below \(T\ns_\Rc\), the isotherms have a flat portion, as shown in Fig. [PVTb], corresponding to a two-phase region where liquid and vapor coexist. In the \((p,T)\) plane, sketched for \(\RH\ns_2\RO\) in Fig. [H2Opd] and shown for \(\RC\RO\ns_2\) in Fig. [PTCO2], this liquid-vapor phase coexistence occurs along a curve, called the vaporization (or boiling) curve. The density changes discontinuously across this curve; for \(\RH\ns_2\RO\), the liquid is approximately 1000 times denser than the vapor at atmospheric pressure. The density discontinuity vanishes at the critical point. Note that one can continuously transform between liquid and vapor phases, without encountering any phase transitions, by going around the critical point and avoiding the two-phase region.
In addition to liquid-vapor coexistence, solid-liquid and solid-vapor coexistence also occur, as shown in Fig. [PVTa]. The triple point \((\RT\ns_\Rt, p\ns_\Rt)\) lies at the confluence of these three coexistence regions. For \(\RH\ns_2\RO\), the location of the triple point and critical point are given by \[\begin{aligned} \RT\ns_\Rt &=273.16\,\RK & T\ns_\Rc&=647\,\RK\\ \Rp\ns_\Rt&=611.7\,{Pa}= 6.037\times 10^{-3}\,{atm} & \Rp\ns_\Rc&=22.06\,{MPa}=217.7\,{atm}\end{aligned}\]
The Clausius-Clapeyron relation
Recall that the homogeneity of \(E(S,V,N)\) guaranteed \(E=TS-pV+\mu N\), from Euler’s theorem. It also guarantees a relation between the intensive variables \(T\), \(p\), and \(\mu\), according to Equation [GDRa]. Let us define \(g\equiv G/\nu=\NA\mu\), the Gibbs free energy per mole. Then \[dg=-s\,dT + v\,dp\ ,\] where \(s=S/\nu\) and \(v=V/\nu\) are the molar entropy and molar volume, respectively. Along a coexistence curve between phase #1 and phase #2, we must have \(g\ns_1=g\ns_2\), since the phases are free to exchange energy and particle number, they are in thermal and chemical equilibrium. This means \[dg\ns_1=-s\ns_1\,dT + v\ns_1\,dp = -s\ns_2\,dT + v\ns_2\,dp =dg\ns_2\ .\] Therefore, along the coexistence curve we must have \[\bigg({d p\over d T}\bigg)\ns_{coex}={s\ns_2-s\ns_1\over v\ns_2-v\ns_1}={\ell\over T\,\RDelta v}\ ,\] where \[\ell\equiv T\,\RDelta s = T\,(s\ns_2-s\ns_1)\] is the molar latent heat of transition. A heat \(\ell\) must be supplied in order to change from phase #1 to phase #2, even without changing \(p\) or \(T\). If \(\ell\) is the latent heat per mole, then we write \({\tilde \ell}\) as the latent heat per gram: \({\tilde \ell}=\ell/M\), where \(M\) is the molar mass.
Along the liquid-gas coexistence curve, we typically have \(v\ns_{gas}\gg v\ns_{liquid}\), and assuming the vapor is ideal, we may write \(\RDelta v\approx v\ns_{gas}\approx RT/p\). Thus, \[\bigg({d p\over d T}\bigg)\ns_{liq-gas}={\ell\over T\,\RDelta v}\approx {p\,\ell\over R T^2}\ .\] If \(\ell\) remains constant throughout a section of the liquid-gas coexistence curve, we may integrate the above equation to get \[{dp\over p} = {\ell\over R}\,{dT\over T^2} \qquad\Longrightarrow\qquad p(T)=p(T\ns_0)\,e^{\ell/R T\ns_0}\,e^{-\ell/RT}\ .\]
Liquid-solid line in \(\RH_2\RO\)
Life on planet earth owes much of its existence to a peculiar property of water: the solid is less dense than the liquid along the coexistence curve. For example at \(T=273.1\,\RK\) and \(p=1\,\)atm, \[{\tilde v}\ns_{water}=1.00013\,{cm}^3/\Rg \qquad,\qquad {\tilde v}\ns_{ice}=1.0907\,{cm}^3/\Rg\ .\] The latent heat of the transition is \({\tilde\ell}=333\,\RJ/\Rg = 79.5\,{cal}/\Rg\). Thus, \[\begin{split} \bigg({d p\over d T}\bigg)\ns_{liq-sol}&=
Callstack:
at (Bookshelves/Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics/Book:_Thermodynamics_and_Statistical_Mechanics_(Arovas)/02:_Thermodynamics/2.11:_Phase_Transitions_and_Phase_Equilibria), /content/body/div[3]/p[1]/span, line 1, column 1

Does the Clausius-Clapeyron relation explain how we can skate on ice? When my daughter was seven years old, she had a mass of about \(M=20\,\)kg. Her ice skates had blades of width about \(5\,\)mm and length about \(10\,\)cm. Thus, even on one foot, she imparted an additional pressure of only \[\RDelta p={Mg\over A}\approx {20\,{kg}\times 9.8\,{\Rm/\Rs^2}\over (5\times 10^{-3}\,\Rm)\times (10^{-1}\,\Rm)} = 3.9\times 10^{5}\,{Pa}=3.9\,{atm}\ .\] The corresponding change in the melting temperature is thus minuscule: \(\RDelta T\ns_{melt}\approx -0.03^\circ\,\RC\).
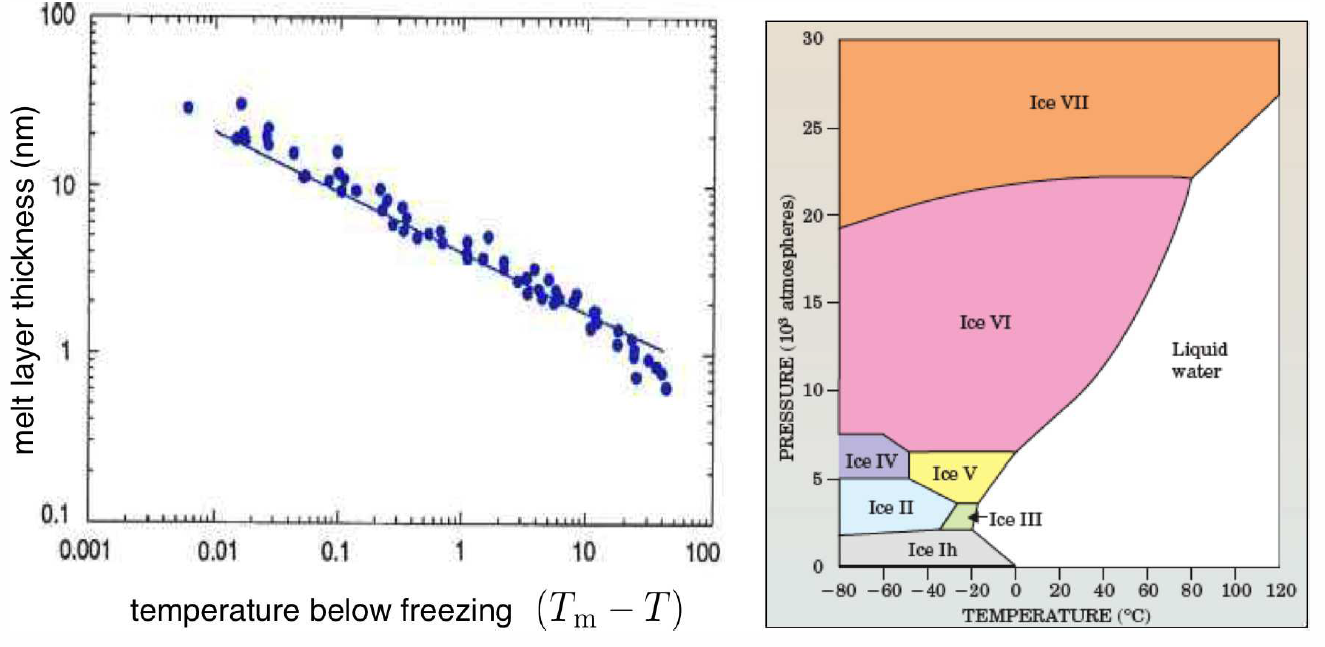
So why could my daughter skate so nicely? The answer isn’t so clear!14 There seem to be two relevant issues in play. First, friction generates heat which can locally melt the surface of the ice. Second, the surface of ice, and of many solids, is naturally slippery. Indeed, this is the case for ice even if one is standing still, generating no frictional forces. Why is this so? It turns out that the Gibbs free energy of the ice-air interface is larger than the sum of free energies of ice-water and water-air interfaces. That is to say, ice, as well as many simple solids, prefers to have a thin layer of liquid on its surface, even at temperatures well below its bulk melting point. If the intermolecular interactions are not short-ranged15, theory predicts a surface melt thickness \(d\propto (T\ns_\Rm-T)^{-1/3}\). In Fig. [surfmelt] we show measurements by Gilpin (1980) of the surface melt on ice, down to about \(-50^\circ\,\)C. Near \(0^\circ\,\RC\) the melt layer thickness is about \(40\,\)nm, but this decreases to \(\sim 1\,\)nm at \(T=-35^\circ\,\)C. At very low temperatures, skates stick rather than glide. Of course, the skate material is also important, since that will affect the energetics of the second interface. The 19th century novel, Hans Brinker, or The Silver Skates by Mary Mapes Dodge tells the story of the poor but stereotypically decent and hardworking Dutch boy Hans Brinker, who dreams of winning an upcoming ice skating race, along with the top prize: a pair of silver skates. All he has are some lousy wooden skates, which won’t do him any good in the race. He has money saved to buy steel skates, but of course his father desperately needs an operation because – I am not making this up – he fell off a dike and lost his mind. The family has no other way to pay for the doctor. What a story! At this point, I imagine the suspense must be too much for you to bear, but this isn’t an American Literature class, so you can use Google to find out what happens (or rent the 1958 movie, directed by Sidney Lumet). My point here is that Hans’ crappy wooden skates can’t compare to the metal ones, even though the surface melt between the ice and the air is the same. The skate blade material also makes a difference, both for the interface energy and, perhaps more importantly, for the generation of friction as well.
Slow melting of ice : a quasistatic but irreversible process
Suppose we have an ice cube initially at temperature \(T\ns_0 < \Theta \equiv 273.15\,\RK\) ( \(\Theta=0^\circ\,\RC\)) and we toss it into a pond of water. We regard the pond as a heat bath at some temperature \(T\ns_1>\Theta\). Let the mass of the ice be \(M\). How much heat \(Q\) is absorbed by the ice in order to raise its temperature to \(T\ns_1\)? Clearly \[Q=M {\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S}(\Theta-T\ns_0) + M {\tilde \ell} + M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L} (T\ns_1-\Theta)\ ,\] where \({\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S}\) and \({\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L}\) are the specific heats of ice (solid) and water (liquid), respectively16, and \({\tilde\ell}\) is the latent heat of melting per unit mass. The pond must give up this much heat to the ice, hence the entropy of the pond, discounting the new water which will come from the melted ice, must decrease: \[\RDelta S\ns_{pond}=-{Q\over T\ns_1}\ .\]
Now we ask what is the entropy change of the \(\RH\ns_2\RO\) in the ice. We have \[\begin{split} \RDelta S\ns_{ice}&=\int\!{\dbar Q\over T} = \int\limits_{T\ns_0}^{\Theta}\!\!dT\,{M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S}\over T} + {M{\tilde \ell}\over \Theta} + \int\limits_{\Theta}^{T\ns_1}\!\!dT\,{M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L}\over T}\\ &=M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S} \ln\!\bigg({\Theta\over T\ns_0}\bigg) + {M{\tilde\ell}\over \Theta} + M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L} \ln\!\bigg({T\ns_1\over \Theta}\bigg) \ . \end{split}\] The total entropy change of the system is then \[\begin{split} \RDelta S\ns_{total}&=\RDelta S\ns_{pond} + \RDelta S\ns_{ice}\\ &=M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S} \ln\!\bigg({\Theta\over T\ns_0}\bigg) - M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S} \bigg({\Theta-T\ns_0\over T\ns_1}\bigg) + M{\tilde\ell}\,\bigg({1\over \Theta}-{1\over T\ns_1}\bigg) + M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L} \ln\!\bigg({T\ns_1\over \Theta}\bigg) - M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L}\bigg( {T\ns_1-\Theta\over T\ns_1}\bigg) \end{split}\] Now since \(T\ns_0<\Theta <T\ns_1\), we have \[M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S} \bigg({\Theta-T\ns_0\over T\ns_1}\bigg) < M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S} \bigg({\Theta-T\ns_0\over \Theta}\bigg)\ .\] Therefore, \[\RDelta S > M{\tilde\ell}\,\bigg({1\over \Theta}-{1\over T\ns_1}\bigg) + M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{S}\, f\big(T\ns_0/\Theta\big) + M{\tilde c}\ns_\ssr{L}\, f\big(\Theta/T\ns_1\big)\ ,\] where \(f(x)=x-1-\ln x\). Clearly \(f'(x)=1-x^{-1}\) is negative on the interval \((0,1)\), which means that the maximum of \(f(x)\) occurs at \(x=0\) and the minimum at \(x=1\). But \(f(0)=\infty\) and \(f(1)=0\), which means that \(f(x)\ge 0\) for \(x\in [0,1]\). Since \(T\ns_0 < \Theta < T\ns_1\) , we conclude \(\RDelta S\ns_{total} > 0\).
Gibbs phase rule
Equilibrium between two phases means that \(p\), \(T\), and \(\mu(p,T)\) are identical. From \[\mu\ns_1(p,T)=\mu\ns_2(p,T)\ ,\] we derive an equation for the slope of the coexistence curve, the Clausius-Clapeyron relation. Note that we have one equation in two unknowns \((T,p)\), so the solution set is a curve. For three phase coexistence, we have \[\mu\ns_1(p,T)=\mu\ns_2(p,T)=\mu\ns_3(p,T)\ ,\] which gives us two equations in two unknowns. The solution is then a point (or a set of points). A critical point also is a solution of two simultaneous equations: \[\hbox{critical point}\quad\Longrightarrow\quad v\ns_1(p,T)=v\ns_2(p,T) \quad,\quad \mu\ns_1(p,T)=\mu\ns_2(p,T)\ .\] Recall \(v=\NA\big({\pz\mu\over\pz p}\big)\ns_T\). Note that there can be no four phase coexistence for a simple \(p\)-\(V\)-\(T\) system.
Now for the general result. Suppose we have \(\sigma\) species, with particle numbers \(N\ns_a\), where \(a=1,\ldots,\sigma\). It is useful to briefly recapitulate the derivation of the Gibbs-Duhem relation. The energy \(E(S,V,N\ns_1,\ldots,N\ns_\sigma)\) is a homogeneous function of degree one: \[E(\lambda S,\lambda V,\lambda N\ns_1,\ldots,\lambda N\ns_\sigma)=\lambda E(S,V,N\ns_1,\ldots,N\ns_\sigma)\ .\] From Euler’s theorem for homogeneous functions (just differentiate with respect to \(\lambda\) and then set \(\lambda=1\)), we have \[E=TS-p\,V+\sum_{a=1}^\sigma \mu\ns_a\, N\ns_a\ .\] Taking the differential, and invoking the First Law, \[dE=T\,dS - p\,dV + \sum_{a=1}^\sigma \mu\ns_a \,dN\ns_a\ ,\] we arrive at the relation \[S\,dT - V dp + \sum_{a=1}^\sigma N\ns_a\,d\mu\ns_a =0\ ,\] of which Equation [GDR] is a generalization to additional internal ‘work’ variables. This says that the \(\sigma+2\) quantities \((T,p,\mu\ns_1,\ldots,\mu\ns_\sigma)\) are not all independent. We can therefore write \[\mu\ns_\sigma=\mu\ns_\sigma\big(T,p,\mu\ns_1,\ldots,\mu\ns_{\sigma-1}\big)\ .\]
If there are \(\varphi\) different phases, then in each phase \(j\), with \(j=1,\ldots,\varphi\), there is a chemical potential \(\mu^{(j)}_a\) for each species \(a\). We then have \[\mu^{(j)}_\sigma=\mu^{(j)}_\sigma\Big(T,p,\mu^{(j)}_1,\ldots,\mu^{(j)}_{\sigma-1}\Big)\ .\] Here \(\mu_a^{(j)}\) is the chemical potential of the \(a^\ssr{th}\) species in the \(j^\ssr{th}\) phase. Thus, there are \(\varphi\) such equations relating the \(2+\varphi\,\sigma\) variables \(\big(T,p,\big\{\mu^{(j)}_a\big\}\big)\), meaning that only \(2+\varphi\,(\sigma-1)\) of them may be chosen as independent. This, then, is the dimension of ‘thermodynamic space’ containing a maximal number of intensive variables: \[d\ns_\ssr{TD}(\sigma,\varphi)=2+\varphi\,(\sigma-1)\ .\] To completely specify the state of our system, we of course introduce a single extensive variable, such as the total volume \(V\). Note that the total particle number \(N=\sum_{a=1}^\sigma N\ns_a\) may not be conserved in the presence of chemical reactions!
Now suppose we have equilibrium among \(\varphi\) phases. We have implicitly assumed thermal and mechanical equilibrium among all the phases, meaning that \(p\) and \(T\) are constant. Chemical equilibrium applies on a species-by-species basis. This means \[\mu_a^{(j)}=\mu_a^{(j')} \label{phaseq}\] where \(j,j'\in\{1,\ldots,\varphi\}\). This gives \(\sigma(\varphi-1)\) independent equations equations17. Thus, we can have phase equilibrium among the \(\varphi\) phases of \(\sigma\) species over a region of dimension \[\begin{split} d\ns_\ssr{PE}(\sigma,\varphi)&=2+\varphi\,(\sigma-1)-\sigma\,(\varphi-1)\\ &=2+\sigma-\varphi\ . \end{split}\] Since \(d_\ssr{PE}\ge 0\), we must have \(\varphi\le \sigma+2\). Thus, with two species (\(\sigma=2\)), we could have at most four phase coexistence.
If the various species can undergo \(\rho\) distinct chemical reactions of the form \[\zeta^{(r)}_1\,\RA\ns_1 + \zeta^{(r)}_2\,\RA\ns_2 + \cdots + \zeta^{(r)}_\sigma\,\RA\ns_\sigma=0\ ,\] where \(\RA\ns_a\) is the chemical formula for species \(a\), and \(\zeta^{(r)}_a\) is the stoichiometric coefficient for the \(a^\ssr{th}\) species in the \(r^\ssr{th}\) reaction, with \(r=1,\ldots,\rho\), then we have an additional \(\rho\) constraints of the form \[\sum_{a=1}^\sigma\zeta^{(r)}_a\,\mu^{(j)}_a=0\ . \label{reacon}\] Therefore, \[d\ns_\ssr{PE}(\sigma,\varphi,\rho)=2+\sigma-\varphi-\rho\ .\] One might ask what value of \(j\) are we to use in Equation \ref{reacon}, or do we in fact have \(\varphi\) such equations for each \(r\)? The answer is that Equation [phaseq] guarantees that the chemical potential of species \(a\) is the same in all the phases, hence it doesn’t matter what value one chooses for \(j\) in Equation [reacon].
Let us assume that no reactions take place, \(\rho=0\), so the total number of particles \(\sum_{b=1}^\sigma N\ns_b\) is conserved. Instead of choosing \((T,p,\mu\ns_1,\ldots,\mu^{(j)}_{\sigma-1})\) as \(d\ns_\ssr{TD}\) intensive variables, we could have chosen \((T,p,\mu\ns_1,\ldots,x^{(j)}_{\sigma-1})\), where \(x\ns_a=N\ns_a/N\) is the concentration of species \(a\).
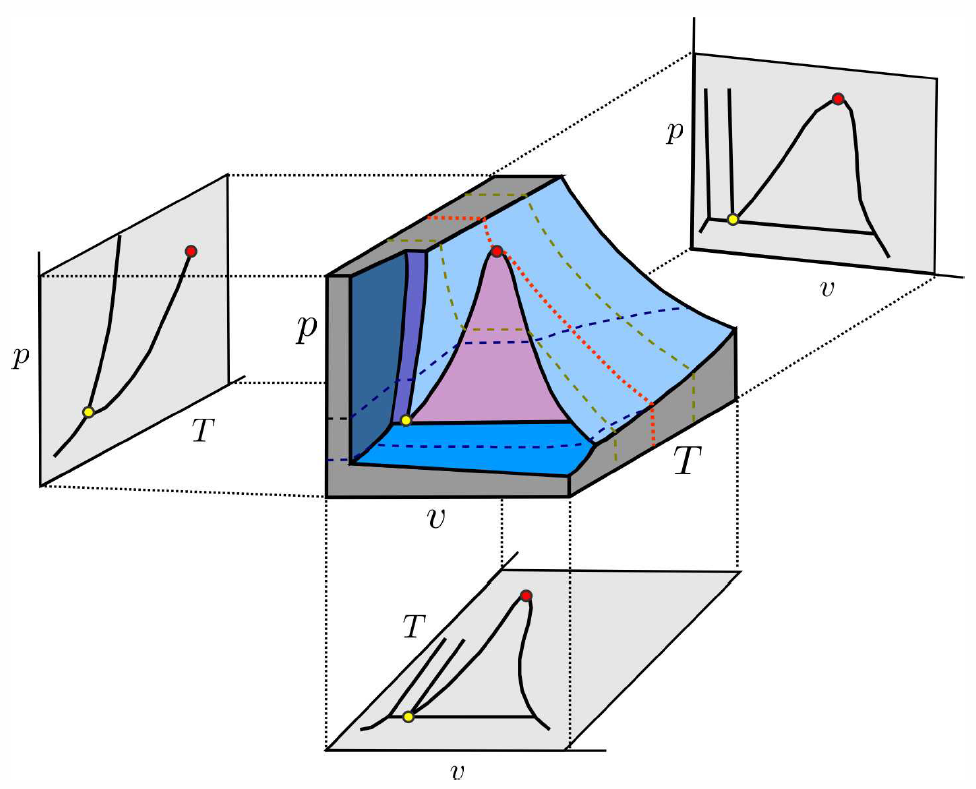
Why do phase diagrams in the \((p,v)\) and \((T,v)\) plane look different than those in the \((p,T)\) plane?18 For example, Fig. [PVTc] shows projections of the \(p\)-\(v\)-\(T\) surface of a typical single component substance onto the \((T,v)\), \((p,v)\), and \((p,T)\) planes. Coexistence takes place along curves in the \((p,T)\) plane, but in extended two-dimensional regions in the \((T,v)\) and \((p,v)\) planes. The reason that \(p\) and \(T\) are special is that temperature, pressure, and chemical potential must be equal throughout an equilibrium phase if it is truly in thermal, mechanical, and chemical equilibrium. This is not the case for an intensive variable such as specific volume \(v=\NA V/N\) or chemical concentration \(x\ns_a=N\ns_a/N\).


