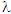 = c/ f = c/ f |
wavelength, frequency, and speed |
Chapter 2 |
| E = hf |
energy and frequency |
Ephoton =  Eelectron Eelectron |
energy of photon emitted/absorbed by atom |
| En = -13.6/n2 |
energy levels of atom |
T = 2.9e-3/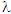 |
temperature and peak wavelength |
F =  T4 T4 |
brightness and temperature |
A =  r2 r2 |
area and radius |
Chapter 3 |
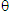 = 1.22 = 1.22 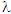 /D /D |
resolution |
| v = d/t |
speed, distance, and time |
Chapter 4 |
z =  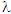 / /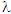 |
redshift |
| v = cz |
velocity and redshift |
| t = E/L |
stellar lifetime |
Chapter 5 |
| E = mc2 |
energy and mass |
| t ~ m-2 |
stellar lifetime and mass |
| L ~ m3 |
stellar mass and luminosity |
| d = 1/a |
parallax angle and distance |
Chapter 6 |
d = S/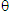 |
small angle formula |
F= L/4 d2 d2 |
inverse square law |
| F = ma |
Newton's second law |
Chapter 7 |
| Fg = mg |
Weight and mass |
| ac = v2/r |
Centripetal acceleration |
| Fg = Gm1m2/r2 |
Newton's law of gravity |
| PE = mgh |
Potential energy (non-relativistic) |
| KE = ½ mv2 |
Kinetic energy (non-relativistic) |
| Efinal = Einitial |
Conservation of energy |
| vescape = (2GM/R)½ |
Escape velocity |
| v ∝ r |
Rotation of rigid disk |
Chapter 8 |
| v ∝ 1/r |
Rotation of water around drain |
| v ∝ constant |
Rotation of cars on roundabout |
| v ∝ 1/r½ |
Keplerian rotation (planets) |
| v2 = GM/r |
Relationship of enclosed mass to velocity and distance |
| M = ρV |
Mass, density, and volume |
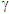 = 1/√(1-v2/c2) = 1/√(1-v2/c2) |
gamma factor |
Chapter 9 |
 t’ = t’ = 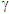  t t |
time dilation |
L’ = L/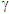 |
length contraction |
d2 =  x2 + x2 +  y2 y2 |
Pythagorean Theorem |
s2 =  x2 – c( x2 – c( t)2 t)2 |
spacetime interval |
| E = mc2 |
mass and rest energy |
E = 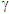 E0 E0 |
total energy and rest energy |
| g=GMR2 |
Surface gravity |
Chapter 10 |
| d=v0t+12at2 |
Distance and acceleration |
| v=at |
Velocity and acceleration |
| t=t0(1−gHc2) |
Time dilation (weak field approximation) |
| f=f0(1−gHc2) |
Gravitational redshift (weak field approximation, frequency, photon traveling upward) |
| λ=λ0(1−gHc2) |
Gravitational redshift (weak field approximation, wavelength) |
| f=f0√1−2GMRc2 |
Gravitational redshift (full expression, frequency) |
| λ=λ0√1−2GMRc2 |
Gravitational redshift (full expression, wavelength) |
| d2=(Δx)2+(Δy)2 |
Pythagorean theorem |
| d2=(RΔθ)2+cos2θ(RΔα)2 |
Distance on a sphere |
| d2=(Δx)2+(Δy)2+(Δz)2 |
Pythagorean Theorem in 3-D |
| s2=(Δx)2+(Δy)2+(Δz)2−(cΔt)2 |
Spacetime interval in flat space |
| s2=(1−2GMrc2)−1[(Δx)2+(Δy)2+(Δz)2]−(1−2GMrc2)(cΔt)2 |
Spacetime interval in spherically curved space |
| θ=2GMbc2 |
Angle of deflection of light |
| Pgw=25(GMRc2)5(mM)2(c5G) |
Power emitted by gravitational waves |
| G=8πG T/c4 |
Einstein equation |
| RS=2GMc2 |
Schwarzschild radius |
Chapter 11 |
| s2=(1−RSd)−1(Δd)2−(1−RSd)(cΔt)2 |
Spacetime interval in a spherically symmetric space (Schwarzschild interval) |
| Tbh=1.23×1023M |
Temperature of a black hole |
| ΔEΔt≥h4π |
Uncertainty principle |
| L=3.56×1032M2 |
Luminosity of a blackhole |
| t≈2.5×10−16M3 |
Evaporation time |
| ΔmΔt=−2Lc2 |
Accretion rate |
| Ledd=6.3MBH |
Eddington luminosity |
| α=4GMbc2 |
Deflection angle (full) |
Chapter 12 |
| θE=√(4GM(b)c2)(DLSDLODSO) |
Einstein radius |
| θ2−xθ−θ2E=0 |
Lens equation |
| m=1[1−(θEθ)4] |
Magnification for a point-mass lens |
| v=H0d |
Hubble law |
Chapter 13 |
| v=cz |
Cosmological redshift |
| dphysical(t)=dcomoving(t)S(t) |
Comoving coordinates |
| 1+z=S(tobserved)S(temitted) |
Ratio of scale factors |
| t=1H0 |
Hubble time (age) |
| H2−8πGρ3=−kc2S2 |
Friedman equation |
| d = cz/H0 |
distance and redshift |
Chapter 14 |
| Te / To = 1 + z = So / Se |
Temperature, redshift, and scale factor |
Chapter 15 |
| E ~ kT |
energy and temperature |
Chapter 16 |
| T ~ mc2/k |
temperature of Universe and mass of particle in reaction |
|
Constants
|
Name |
| c = 3 x 108 m/s = 3 x 105 km/s |
speed of light |
| h = 6.63 x 10-34 J s = 4.136e-15 eV s |
Planck’s constant |
| G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 |
Universal gravitational constant |
| kB = 1.38 × 10-23 J/K |
Boltzmann's constant |
| tplanck ~ 10-43 s |
Planck time |
| tplanck ~ 4 × 10-35 m |
Planck length |
| me = 9.1 × 10-31 kg |
mass of an electron |
|
Conversions
|
Units |
| 1 km = 1000 m |
km and meters |
| 1 km = 0.6 mi |
km and miles |
| 1 AU = 1.5 x 1011 m = 1.5 x 108 km |
AU and meters and km |
| 1 ly = 9.5 x 1015 m = 9.5 x 1012 km |
light-years and meters and km |
| 1 ly = 6.3 x 104 AU |
light-years and AU |
| 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J |
eV and joules |
| 1 degree = 60 arcmin |
degrees and arcminutes |
| 1 arcmin = 60 arcsec |
arcminutes and arcseconds |
| 1 angstrom (Å) = 1 x 10-10 meters |
angstroms and meters |
| 1 pc = 3.26 ly |
parsecs and light-years |
| 1 N = 0.2248 pounds |
newtons and pounds |
| 1 kpc = 3.086 x 1019 m |
kiloparsecs and meters |
| 1 solar mass = 2 × 1030 kg |
solar masses and kg |
| 1 Mpc = 3.09 x 1022 m |
megaparsecs and meters |
| 1 radian = 2.06 x 105 arcsecond |
radians and arcsec |
| 1 Mpc = 3.09 × 1019 km |
megaparsecs and km |
|
Units (abbreviation)
|
Type of quantity |
| meters (m) |
length (SI) |
| kilograms (kg) |
mass (SI) |
| second (s) |
time (SI) |
| meters per second (m/s) |
speed (SI) |
| kelvin (K) |
temperature (SI) |
| miles (mi) |
length |
| astronomical unit (AU) |
length |
| year (yr) |
time |
| light-year (ly) |
length |
| light-minutes |
length |
| light-seconds |
length |
| g/cm3 |
density |
| solar masses |
mass |
| hertz (Hz) = cycles/s = 1/s = s-1 |
frequency (SI) |
| joules (J) |
energy (SI) |
| electron volts (eV) |
energy |
| watts (W) = J/s |
power |
| radians |
angle |
| degrees |
angle |
| arcmin |
angle |
| arcsec |
angle |
| angstrom (Å) |
length |
| parsec (pc) |
length |
| m/s2 |
acceleration (SI) |
| newton (N) = kg m/s2 |
force (SI) |
| joules (J) = N m |
energy (SI) |
| μK micro Kelvin = 10-6 K |
temperature |


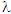 = c/ f
= c/ f  Eelectron
Eelectron T4
T4 r2
r2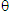 = 1.22
= 1.22 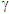 = 1/√(1-v2/c2)
= 1/√(1-v2/c2)