5.5: The Equation of Transfer
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
The equation of transfer deals with the transfer of radiation through an atmosphere that is simultaneously absorbing, scattering and emitting.
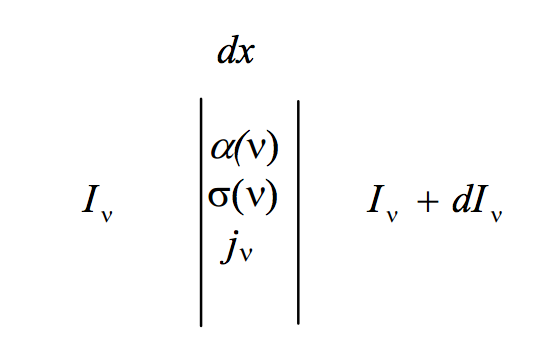
FIGURE V.1
Suppose that, between x and x+dx the absorption coefficient and the scattering coefficient at frequency ν are α(ν) and σ(ν), and the emission coefficient per unit frequency interval is jνdν. In this interval, suppose that the specific intensity per unit frequency interval increases from Iν to Iν+dIν (dIν might be positive or negative). The specific intensity will be reduced by absorption and scattering and increased by emission. Thus:
dIν=−[Iνα(ν)+Iνσ(ν)−jν(ν)]dx.
This is one form - the most basic form - of the equation of transfer. Notice that α and σ do not have a subscript.


