3.4: Projectile Motion
- Page ID
- 1494
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify and explain the properties of a projectile, such as acceleration due to gravity, range, maximum height, and trajectory.
- Determine the location and velocity of a projectile at different points in its trajectory.
- Apply the principle of independence of motion to solve projectile motion problems.
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile, and its path is called its trajectory. The motion of falling objects, as covered in Problem-Solving Basics for One-Dimensional Kinematics, is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movement. In this section, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, such as that of a football or other object for which air resistance is negligible.
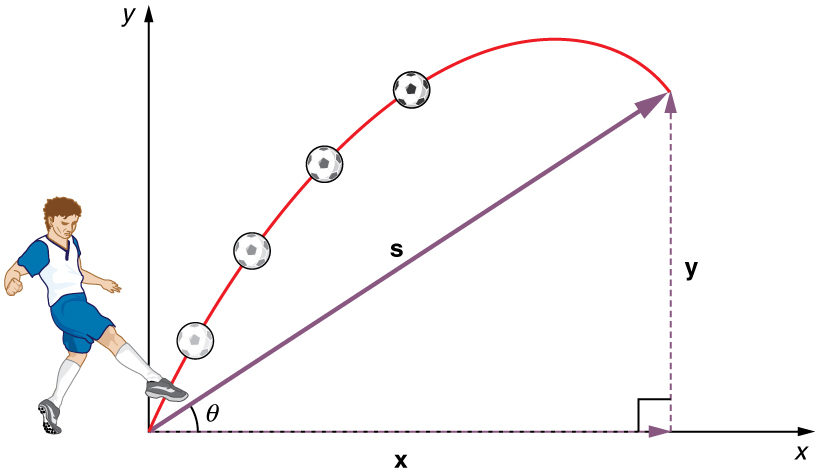
The most important fact to remember here is that motions along perpendicular axes are independent and thus can be analyzed separately. This fact was discussed in Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction, where vertical and horizontal motions were seen to be independent. The key to analyzing two-dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions, one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. (This choice of axes is the most sensible, because acceleration due to gravity is vertical—thus, there will be no acceleration along the horizontal axis when air resistance is negligible.) As is customary, we call the horizontal axis the x-axis and the vertical axis the y-axis. Figure illustrates the notation for displacement, where \(\displaystyle s\) is defined to be the total displacement and \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle y\) are its components along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. The magnitudes of these vectors are s, x, and y. (Note that in the last section we used the notation \(\displaystyle A\) to represent a vector with components \(\displaystyle A_x\) and \(\displaystyle A_y\). If we continued this format, we would call displacement \(\displaystyle s\) with components \(\displaystyle s_x\) and \(\displaystyle s_y\). However, to simplify the notation, we will simply represent the component vectors as \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle y\).)
Of course, to describe motion we must deal with velocity and acceleration, as well as with displacement. We must find their components along the x- and y-axes, too. We will assume all forces except gravity (such as air resistance and friction, for example) are negligible. The components of acceleration are then very simple: \(\displaystyle a_y=–g=–9.80 m/s^2\)(. (Note that this definition assumes that the upwards direction is defined as the positive direction. If you arrange the coordinate system instead such that the downwards direction is positive, then acceleration due to gravity takes a positive value.) Because gravity is vertical, \(\displaystyle a_x=0\). Both accelerations are constant, so the kinematic equations can be used.
REVIEW OF KINEMATIC EQUATIONS (CONSTANT )
\(\displaystyle x=x_0+\bar{v}t\)
\(\displaystyle \bar{v}=\frac{v_0+v}{2}\)
\(\displaystyle v=v_0+at\)
\(\displaystyle x=x_0+v_0t+\frac{1}{2}at^2\)
\(\displaystyle v^2=v^2_0+2a(x−x_0)\).
Given these assumptions, the following steps are then used to analyze projectile motion:
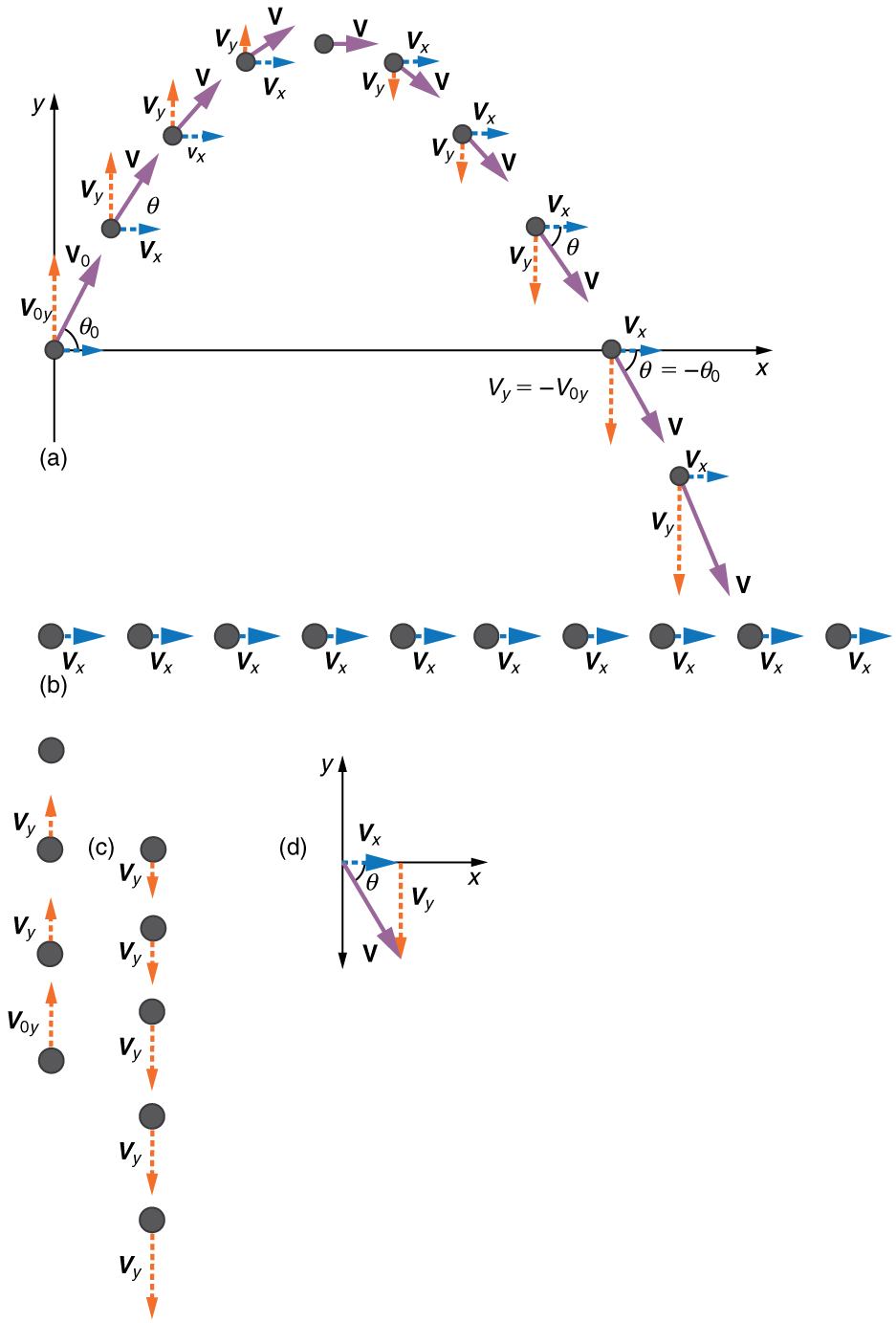
Step 1. Resolve or break the motion into horizontal and vertical components along the x- and y-axes. These axes are perpendicular, so \(\displaystyle A_x=Acosθ\) and \(\displaystyle A_y=Asinθ\) are used. The magnitude of the components of displacement \(\displaystyle s\) along these axes are \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle y\). The magnitudes of the components of the velocity \(\displaystyle v\) are \(\displaystyle v_x=vcosθ\) and \(\displaystyle v_y=vsinθ\), where \(\displaystyle v\) is the magnitude of the velocity and θ is its direction, as shown in Figure. Initial values are denoted with a subscript 0, as usual.
Step 2. Treat the motion as two independent one-dimensional motions, one horizontal and the other vertical. The kinematic equations for horizontal and vertical motion take the following forms:
\(\displaystyle \text{Horizontal Motion}(a_x=0)\)
\(\displaystyle x=x_0+v_xt\)
\(\displaystyle v_x=v_{0x}=v_x=\text{velocity is a constant}\).
\(\displaystyle \text{Vertical Motion(assuming positive is up}a_y=−g=−9.80m/s^2)\)
\(\displaystyle y=y_0+\frac{1}{2}(v_{0y}+v_y)t\)
\(\displaystyle v_y=v_{0y}−gt\)
\(\displaystyle y=y_0+v_{0y}t−\frac{1}{2}gt^2\)
\(\displaystyle v^2_y=v^2_{0y}−2g(y−y_0)\).
Step 3. Solve for the unknowns in the two separate motions—one horizontal and one vertical. Note that the only common variable between the motions is time t. The problem solving procedures here are the same as for one-dimensional kinematics and are illustrated in the solved examples below.
Step 4. Recombine the two motions to find the total displacement \(\displaystyle s\) and velocity \(\displaystyle v\). Because the x - and y -motions are perpendicular, we determine these vectors by using the techniques outlined in the Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods and employing \(\displaystyle A=\sqrt{A^2_x+A^2_y}\) and \(\displaystyle θ=tan^{−1}(A_y/A_x)\) in the following form, where \(\displaystyle θ\) is the direction of the displacement \(\displaystyle s\) and \(\displaystyle θ_v\) is the direction of the velocity \(\displaystyle v\):
Total displacement and velocity
\(\displaystyle s=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
\(\displaystyle θ=tan^{−1}(y/x)\)
\(\displaystyle v=\sqrt{v^2_x+v^2_y}\)
\(\displaystyle θ_v=tan^{−1}(v_y/v_x)\).
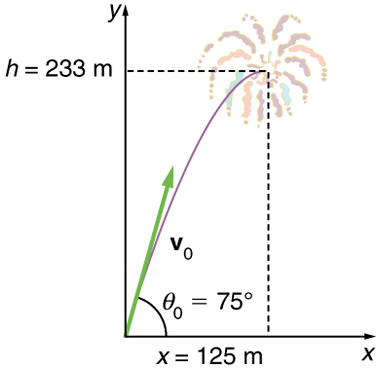
Example \(\displaystyle \PageIndex{1}\): A Fireworks Projectile Explodes High and Away
During a fireworks display, a shell is shot into the air with an initial speed of 70.0 m/s at an angle of 75.0º above the horizontal, as illustrated in Figure. The fuse is timed to ignite the shell just as it reaches its highest point above the ground.
- Calculate the height at which the shell explodes.
- How much time passed between the launch of the shell and the explosion?
- What is the horizontal displacement of the shell when it explodes?
Strategy
Because air resistance is negligible for the unexploded shell, the analysis method outlined above can be used. The motion can be broken into horizontal and vertical motions in which \(\displaystyle a_x=0\) and \(\displaystyle a_y=–g\). We can then define \(\displaystyle x_0\) and \(\displaystyle y_0\) to be zero and solve for the desired quantities.
Solution for (a)
By “height” we mean the altitude or vertical position y above the starting point. The highest point in any trajectory, called the apex, is reached when \(\displaystyle v_y=0\). Since we know the initial and final velocities as well as the initial position, we use the following equation to find \(\displaystyle y\):
\(\displaystyle v^2_y=v^2_{0y}−2g(y−y_0)\).
Because \(\displaystyle y_0\) and \(\displaystyle v_y\) are both zero, the equation simplifies to
\(\displaystyle 0=v^2_{0y}−2gy.\)
Solving for \(\displaystyle y\) gives
\(\displaystyle y=\frac{v^2_{0y}}{2g}\).
Now we must find \(\displaystyle v_{0y}\), the component of the initial velocity in the y-direction. It is given by \(\displaystyle v_{0y}=v_0sinθ\), where \(\displaystyle v_{0y}\) is the initial velocity of 70.0 m/s, and \(\displaystyle θ_0=75.0º\) is the initial angle. Thus,
\(\displaystyle v_{0y}=v_0sinθ_0=(70.0 m/s)(sin 75º)=67.6 m/s.\)
and \(\displaystyle y\) is
\(\displaystyle y=\frac{(67.6 m/s)^2}{2(9.80 m/s^2)}\),
so that
\(\displaystyle y=233m.\)
Discussion for (a)
Note that because up is positive, the initial velocity is positive, as is the maximum height, but the acceleration due to gravity is negative. Note also that the maximum height depends only on the vertical component of the initial velocity, so that any projectile with a 67.6 m/s initial vertical component of velocity will reach a maximum height of 233 m (neglecting air resistance). The numbers in this example are reasonable for large fireworks displays, the shells of which do reach such heights before exploding. In practice, air resistance is not completely negligible, and so the initial velocity would have to be somewhat larger than that given to reach the same height.
Solution for (b)
As in many physics problems, there is more than one way to solve for the time to the highest point. In this case, the easiest method is to use \(\displaystyle y=y_0+\frac{1}{2}(v_{0y}+v_y)t\). Because y0 is zero, this equation reduces to simply
\(\displaystyle y=\frac{1}{2}(v_{0y}+v_y)t\).
Note that the final vertical velocity, \(\displaystyle v_y\), at the highest point is zero. Thus,
\(\displaystyle t=\frac{2y}{(v_{0y}+v_y)}=\frac{2(233 m)}{(67.6 m/s)}=6.90 s.\)
Discussion for (b)
This time is also reasonable for large fireworks. When you are able to see the launch of fireworks, you will notice several seconds pass before the shell explodes. (Another way of finding the time is by using \(\displaystyle y=y_0+v_{0y}t−\frac{1}{2}gt^2\), and solving the quadratic equation for \(\displaystyle t\).)
Solution for (c)
Because air resistance is negligible, \(\displaystyle a_x=0\) and the horizontal velocity is constant, as discussed above. The horizontal displacement is horizontal velocity multiplied by time as given by \(\displaystyle x=x_0+v_xt\), where \(\displaystyle x_0\) is equal to zero:
\(\displaystyle x=v_xt,\)
where \(\displaystyle v_x\) is the x-component of the velocity, which is given by \(\displaystyle v_x=v_0cosθ_0\). Now,
\(\displaystyle v_x=v_0cosθ_0=(70.0 m/s)(cos 75.0º)=18.1 m/s.\)
The time \(\displaystyle t\) for both motions is the same, and so \(\displaystyle x\) is
\(\displaystyle x=(18.1 m/s)(6.90 s)=125 m.\)
Discussion for (c)
The horizontal motion is a constant velocity in the absence of air resistance. The horizontal displacement found here could be useful in keeping the fireworks fragments from falling on spectators. Once the shell explodes, air resistance has a major effect, and many fragments will land directly below.
In solving part (a) of the preceding example, the expression we found for y is valid for any projectile motion where air resistance is negligible. Call the maximum height \(\displaystyle y=h\); then,
\(\displaystyle h=\frac{v^2_{0y}}{2g}\).
This equation defines the maximum height of a projectile and depends only on the vertical component of the initial velocity.
DEFINING A COORDINATE SYSTEM
It is important to set up a coordinate system when analyzing projectile motion. One part of defining the coordinate system is to define an origin for the \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle y\) positions. Often, it is convenient to choose the initial position of the object as the origin such that \(\displaystyle x_0=0\) and \(\displaystyle y_0=0\). It is also important to define the positive and negative directions in the \(\displaystyle x\) and \(\displaystyle y\) directions. Typically, we define the positive vertical direction as upwards, and the positive horizontal direction is usually the direction of the object’s motion. When this is the case, the vertical acceleration, \(\displaystyle g\), takes a negative value (since it is directed downwards towards the Earth). However, it is occasionally useful to define the coordinates differently. For example, if you are analyzing the motion of a ball thrown downwards from the top of a cliff, it may make sense to define the positive direction downwards since the motion of the ball is solely in the downwards direction. If this is the case, g takes a positive value.
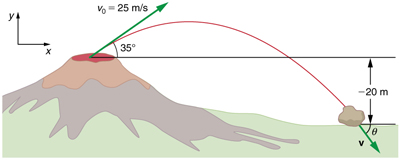
Example \(\displaystyle \PageIndex{2}\): Calculating Projectile Motion: Hot Rock Projectile
Kilauea in Hawaii is the world’s most continuously active volcano. Very active volcanoes characteristically eject red-hot rocks and lava rather than smoke and ash. Suppose a large rock is ejected from the volcano with a speed of 25.0 m/s and at an angle above the horizontal, as shown in Figure. The rock strikes the side of the volcano at an altitude 20.0 m lower than its starting point. (a) Calculate the time it takes the rock to follow this path. (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the rock’s velocity at impact?
Strategy
Again, resolving this two-dimensional motion into two independent one-dimensional motions will allow us to solve for the desired quantities. The time a projectile is in the air is governed by its vertical motion alone. We will solve for \(\displaystyle t\) first. While the rock is rising and falling vertically, the horizontal motion continues at a constant velocity. This example asks for the final velocity. Thus, the vertical and horizontal results will be recombined to obtain \(\displaystyle v\) and \(\displaystyle θ_v\) at the final time t determined in the first part of the example.
Solution for (a)
While the rock is in the air, it rises and then falls to a final position 20.0 m lower than its starting altitude. We can find the time for this by using
\(\displaystyle y=y_0+v_{0y}t−\frac{1}{2}gt^2\).
If we take the initial position \(\displaystyle y_0\) to be zero, then the final position is \(\displaystyle y=−20.0 m\). Now the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity, found from \(\displaystyle v_{0y}=v_0sinθ_0 = (25.0 m/s)(sin 35.0º) = 14.3 m/s.\) Substituting known values yields
\(\displaystyle −20.0 m=(14.3 m/s)t−(4.90 m/s^2)t^2\).
Rearranging terms gives a quadratic equation in \(\displaystyle t\):
\(\displaystyle (4.90 m/s^2)t^2−(14.3 m/s)t−(20.0 m)=0.\)
This expression is a quadratic equation of the form \(\displaystyle at^2+bt+c=0\), where the constants are \(\displaystyle a=4.90, b=–14.3\), and \(\displaystyle c=–20.0.\) Its solutions are given by the quadratic formula:
\(\displaystyle t=\frac{−b±\sqrt{b^2−4ac}}{2a}\).
This equation yields two solutions: \(\displaystyle t=3.96\) and \(\displaystyle t=–1.03\). (It is left as an exercise for the reader to verify these solutions.) The time is \(\displaystyle t=3.96s\) or \(\displaystyle –1.03s\). The negative value of time implies an event before the start of motion, and so we discard it. Thus,
\(\displaystyle t=3.96 s.\)
Discussion for (a)
The time for projectile motion is completely determined by the vertical motion. So any projectile that has an initial vertical velocity of 14.3 m/s and lands 20.0 m below its starting altitude will spend 3.96 s in the air.
Solution for (b)
From the information now in hand, we can find the final horizontal and vertical velocities \(\displaystyle v_x\) and \(\displaystyle v_y\) and combine them to find the total velocity v and the angle \(\displaystyle θ_0\) it makes with the horizontal. Of course, \(\displaystyle v_x\) is constant so we can solve for it at any horizontal location. In this case, we chose the starting point since we know both the initial velocity and initial angle. Therefore:
\(\displaystyle v_x=v_0cosθ_0=(25.0 m/s)(cos 35º)=20.5 m/s.\)
The final vertical velocity is given by the following equation:
\(\displaystyle v_y=v_{0y}−gt\),
where \(\displaystyle v_{0y}\) was found in part (a) to be 14.3 m/s. Thus,
\(\displaystyle v_y=14.3 m/s−(9.80 m/s^2)(3.96 s)\)
so that
\(\displaystyle v_y=−24.5 m/s.\)
To find the magnitude of the final velocity v we combine its perpendicular components, using the following equation:
\(\displaystyle v=\sqrt{v^2_x+v^2_y}=\sqrt{(20.5 m/s)^2+(−24.5 m/s)^2}\),
which gives
\(\displaystyle v=31.9 m/s.\)
The direction θv is found from the equation:
\(\displaystyle θ_v=tan^{−1}(v_y/v_x)\)
so that
\(\displaystyle θ_v=tan^{−1}(−24.5/20.5)=tan^{−1}(−1.19).\)
Thus,
\(\displaystyle θ_v=−50.1º.\)
Discussion for (b)
The negative angle means that the velocity is 50.1º below the horizontal. This result is consistent with the fact that the final vertical velocity is negative and hence downward—as you would expect because the final altitude is 20.0 m lower than the initial altitude. (See Figure.)
One of the most important things illustrated by projectile motion is that vertical and horizontal motions are independent of each other. Galileo was the first person to fully comprehend this characteristic. He used it to predict the range of a projectile. On level ground, we define range to be the horizontal distance traveled by a projectile. Galileo and many others were interested in the range of projectiles primarily for military purposes—such as aiming cannons. However, investigating the range of projectiles can shed light on other interesting phenomena, such as the orbits of satellites around the Earth. Let us consider projectile range further.
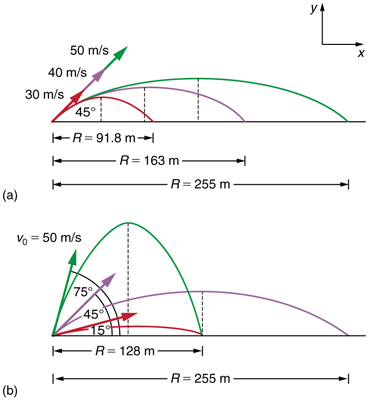
How does the initial velocity of a projectile affect its range? Obviously, the greater the initial speed \(\displaystyle v_0\), the greater the range, as shown in Figure(a). The initial angle \(\displaystyle θ_0\) also has a dramatic effect on the range, as illustrated in Figure(b). For a fixed initial speed, such as might be produced by a cannon, the maximum range is obtained with \(\displaystyle θ_0=45º\). This is true only for conditions neglecting air resistance. If air resistance is considered, the maximum angle is approximately \(\displaystyle 38º\). Interestingly, for every initial angle except \(\displaystyle 45º\), there are two angles that give the same range—the sum of those angles is \(\displaystyle 90º\). The range also depends on the value of the acceleration of gravity \(\displaystyle g\). The lunar astronaut Alan Shepherd was able to drive a golf ball a great distance on the Moon because gravity is weaker there. The range \(\displaystyle R\) of a projectile on level ground for which air resistance is negligible is given by
\(\displaystyle R=\frac{v^2_0sin2θ_0}{g}\),
where \(\displaystyle v_0\) is the initial speed and \(\displaystyle θ_0\) is the initial angle relative to the horizontal. The proof of this equation is left as an end-of-chapter problem (hints are given), but it does fit the major features of projectile range as described.
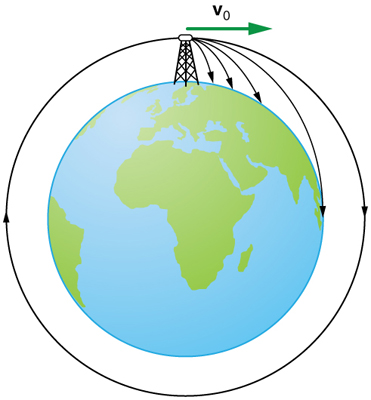
When we speak of the range of a projectile on level ground, we assume that \(\displaystyle R\) is very small compared with the circumference of the Earth. If, however, the range is large, the Earth curves away below the projectile and acceleration of gravity changes direction along the path. The range is larger than predicted by the range equation given above because the projectile has farther to fall than it would on level ground. (See Figure.) If the initial speed is great enough, the projectile goes into orbit. This is called exit velocity. This possibility was recognized centuries before it could be accomplished. When an object is in orbit, the Earth curves away from underneath the object at the same rate as it falls. The object thus falls continuously but never hits the surface. These and other aspects of orbital motion, such as the rotation of the Earth, will be covered analytically and in greater depth later in this text.
Once again we see that thinking about one topic, such as the range of a projectile, can lead us to others, such as the Earth orbits. In Addition of Velocities, we will examine the addition of velocities, which is another important aspect of two-dimensional kinematics and will also yield insights beyond the immediate topic.
PHET EXPLORATIONS: PROJECTILE MOTION
Blast a Buick out of a cannon! Learn about projectile motion by firing various objects. Set the angle, initial speed, and mass. Add air resistance. Make a game out of this simulation by trying to hit a target.

Summary
- Projectile motion is the motion of an object through the air that is subject only to the acceleration of gravity.
- To solve projectile motion problems, perform the following steps:
- Determine a coordinate system. Then, resolve the position and/or velocity of the object in the horizontal and vertical components. The components of position s are given by the quantities x and y, and the components of the velocity v are given by vx=vcosθ and vy=vsinθ, where v is the magnitude of the velocity and θ is its direction.
2. Analyze the motion of the projectile in the horizontal direction using the following equations:
\(\displaystyle \text{Horizontal motion}(a_x=0)\)
\(\displaystyle x=x_0+v_xt\)
\(\displaystyle v_x=v_{0x}=v_x=\text{velocity is a constant}\).
3. Analyze the motion of the projectile in the vertical direction using the following equations:
\(\displaystyle \text{Vertical motion(Assuming positive direction is up;}a_y=−g=−9.80 m/s^2)\)
\(\displaystyle y=y_0+\frac{1}{2}(v_{0y}+v_y)t\)
\(\displaystyle v_y=v_{0y}−gt\)
\(\displaystyle y=y_0+v_{0y}t−\frac{1}{2}gt^2\)
\(\displaystyle v^2_y=v^2_{0y}−2g(y−y_0)\).
4. Recombine the horizontal and vertical components of location and/or velocity using the following equations:
\(\displaystyle s=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\)
\(\displaystyle θ=tan^{−1}(y/x)\)
\(\displaystyle v=\sqrt{v^2_x+v^2_y}\)
\(\displaystyle θ_v=tan^{−1}(v_y/v_x)\).
- The maximum height \(\displaystyle h\) of a projectile launched with initial vertical velocity \(\displaystyle v_{0y}\) is given by
\(\displaystyle h=\frac{v^2_{0y}}{2g}\).
- The maximum horizontal distance traveled by a projectile is called the range. The range \(\displaystyle R\) of a projectile on level ground launched at an angle \(\displaystyle θ_0\) above the horizontal with initial speed \(\displaystyle v_0\) is given by
\(\displaystyle R=\frac{v^2_0sin2θ_0}{g}\).
Glossary
- air resistance
- a frictional force that slows the motion of objects as they travel through the air; when solving basic physics problems, air resistance is assumed to be zero
- kinematics
- the study of motion without regard to mass or force
- motion
- displacement of an object as a function of time
- projectile
- an object that travels through the air and experiences only acceleration due to gravity
- projectile motion
- the motion of an object that is subject only to the acceleration of gravity
- range
- the maximum horizontal distance that a projectile travels
- trajectory
- the path of a projectile through the air


