27.4: Multiple Slit Diffraction
- Page ID
- 2743
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the pattern obtained from diffraction grating.
- Explain diffraction grating effects.
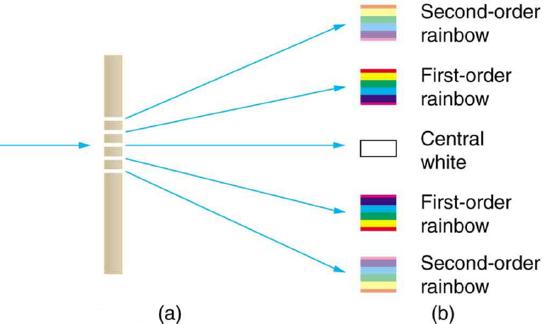
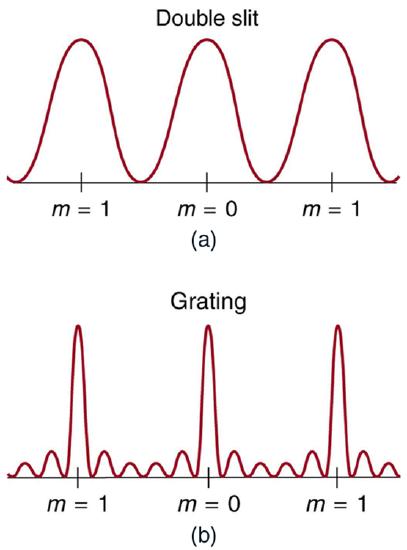
An interesting thing happens if you pass light through a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits, called a diffraction grating. An interference pattern is created that is very similar to the one formed by a double slit (see Figure 1). A diffraction grating can be manufactured by scratching glass with a sharp tool in a number of precisely positioned parallel lines, with the untouched regions acting like slits. These can be photographically mass produced rather cheaply. Diffraction gratings work both for transmission of light, as in Figure 1, and for reflection of light, as on butterfly wings and the Australian opal in Figure 2 or the CD pictured in the opening photograph of this chapter. In addition to their use as novelty items, diffraction gratings are commonly used for spectroscopic dispersion and analysis of light. What makes them particularly useful is the fact that they form a sharper pattern than double slits do. That is, their bright regions are narrower and brighter, while their dark regions are darker. Figure 3 shows idealized graphs demonstrating the sharper pattern. Natural diffraction gratings occur in the feathers of certain birds. Tiny, finger-like structures in regular patterns act as reflection gratings, producing constructive interference that gives the feathers colors not solely due to their pigmentation. This is called iridescence.

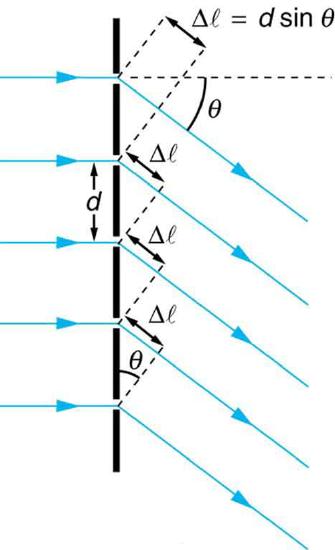
The analysis of a diffraction grating is very similar to that for a double slit (see Figure 4). As we know from our discussion of double slits in "Young's Double Slit Experiment," light is diffracted by each slit and spreads out after passing through. Rays traveling in the same direction (at an angle \(\theta\) relative to the incident direction) are shown in the figure. Each of these rays travels a different distance to a common point on a screen far away. The rays start in phase, and they can be in or out of phase when they reach a screen, depending on the difference in the path lengths traveled. As seen in the figure, each ray travels a distance \(d\sin{\theta}\) different from that of its neighbor, where \(d\) is the distance between slits. If this distance equals an integral number of wavelengths, the rays all arrive in phase, and constructive interference (a maximum) is obtained. Thus, the condition necessary to obtain constructive interference for a diffraction grating is \[d\sin{\theta} = m \lambda, for m=0,1,-1,2,-2,...\left(constructive\right)\label{27.5.1}\] where \(d\) is the distance between slits in the grating, \(\lambda\) is the wavelength of light, and \(m\) is the order of the maximum. Note that this is exactly the same equation as for double slits separated by \(d\). However, the slits are usually closer in diffraction gratings than in double slits, producing fewer maxima at larger angles.
Where are diffraction gratings used? Diffraction gratings are key components of monochromators used, for example, in optical imaging of particular wavelengths from biological or medical samples. A diffraction grating can be chosen to specifically analyze a wavelength emitted by molecules in diseased cells in a biopsy sample or to help excite strategic molecules in the sample with a selected frequency of light. Another vital use is in optical fiber technologies where fibers are designed to provide optimum performance at specific wavelengths. A range of diffraction gratings are available for selecting specific wavelengths for such use.
TAKE-HOME EXPERIMENT: RAINBOWS ON A CD
The spacing \(d\)) of the grooves in a CD or DVD can be well determined by using a laser and the equation \(d\sin{\theta} = m \lambda, for m = 0,1,-1,2,-2,...\) However, we can still make a good estimate of this spacing by using white light and the rainbow of colors that comes from the interference. Reflect sunlight from a CD onto a wall and use your best judgment of the location of a strongly diffracted color to find the separation \(d\).
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Calculating Typical Diffraction Grating Effects
Diffraction gratings with 10,000 lines per centimeter are readily available. Suppose you have one, and you send a beam of white light through it to a screen 2.00 m away. (a) Find the angles for the first-order diffraction of the shortest and longest wavelengths of visible light (380 and 760 nm). (b) What is the distance between the ends of the rainbow of visible light produced on the screen for first-order interference? (See Figure.)
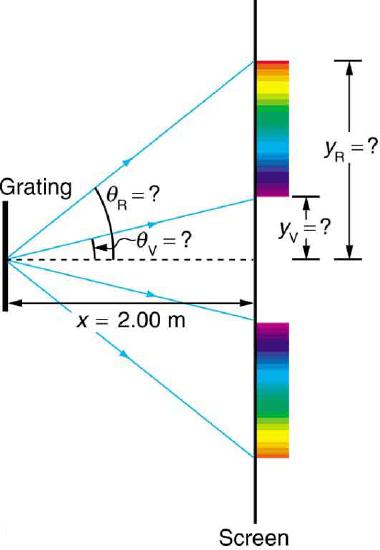
Strategy:
The angles can be found using the equation \[d\sin{\theta} = m \lambda, for m = 0,1,-1,2,-2,...\label{27.5.1}\] once a value for the slit spacing \(d\) has been determined. Since there are 10,000 lines per centimeter, each line is separated by \(1/10,000\) of a centimeter. Once the angles are found, the distances along the screen can be found using simple trigonometry.
Solution for (a):
The distance between slits is \(d = \left(1 cm\right) / 10,000 = 1.00 \times 10^{-4} cm\) or \(1.00 \times 10^{-6} m\). Let us call the two angles \(\theta_{V}\) for violet (380 nm) and \(\theta_{R}\) for red (760 nm). Solving the equation \(d\sin{\theta_{V}} = m \lambda\) for \(\sin{\theta_{V}}\), \[\sin{\theta_{V}} = \frac{m \lambda v}{d}, \label{27.5.2}\] where \(m = 1\) for first order and \(\lambda_{v} = 380 nm = 3.80 \times 10^{-7} m\). Substituting these values gives \[\sin{\theta_{v}} = \frac{3.80 \times 10^{-7} m}{1.00 \times 10^{-6} m} = 0.380.\] Thus the angle \(\theta_{v}\) is \[\theta_{v} = \sin^{-1}{0.380} = 22.33^{\circ}.\] Similarly, \[\sin{\theta_{R}} = \frac{7.60 \times 10^{-7} m}{1.00 \times 10^{-6} m}.\] Thus the angle \(\theta_{R}\) is \[\theta_{R} = \sin^{-1}{0.760} = 49.46^{\circ}.\] Notice that in both equations, we reported the results of these intermediate calculations to four significant figures to use with the calculation in part (b).
Solution for (b):
The distances on the screen are labeled \(y_{v}\) and \(y_{R}\) in the figure. Noting that \(\tan{\theta} = y/x\), we can solve for \(y_{v}\) and \(y_{R}\). That is, \[y_{v} = x \tan{\theta_{v}} = \left( 2.00 m \right) \left(\tan{22.33^{\circ}}\right) = 0.815m \label{25.7.3}\] and \[y_{R} = x \tan{\theta_{R}} = \left( 2.00 m \right) \left( \tan{49.46^{\circ}} \right) = 2.338 m \label{25.7.4}.\] The distance between them is therefore \[y_{R} - y_{v} = 1.52 m.\]
Discussion:
The large distance between the red and violet ends of the rainbow produced from the white light indicates the potential this diffraction grating has as a spectroscopic tool. The more it can spread out the wavelengths (greater dispersion), the more detail can be seen in a spectrum. This depends on the quality of the diffraction grating—it must be very precisely made in addition to having closely spaced lines.
Summary
- A diffraction grating is a large collection of evenly spaced parallel slits that produces an interference pattern similar to but sharper than that of a double slit.
- There is constructive interference for a diffraction grating when \(d\sin{\theta} = m \lambda \left( for m = 0,1,-1,2,-2,...\right)\), where \(d\) is the distance between slits in the grating, \(\lambda\) is the wavelength of light, and \(m\) is the order of the maximum.
Glossary
- constructive interference for a diffraction grating
- occurs when the condition \(d \sin{\theta} = m \lambda \left(for~m = 0,1,-1,2,-2,...\right)\) is satisfied, where \(d\) is the distance between slits in the grating, \(\lambda\) is the wavelength of light, and \(m\) is the order of the maximum
- diffraction grating
- a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits


