4.5: Conductors in Parallel
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
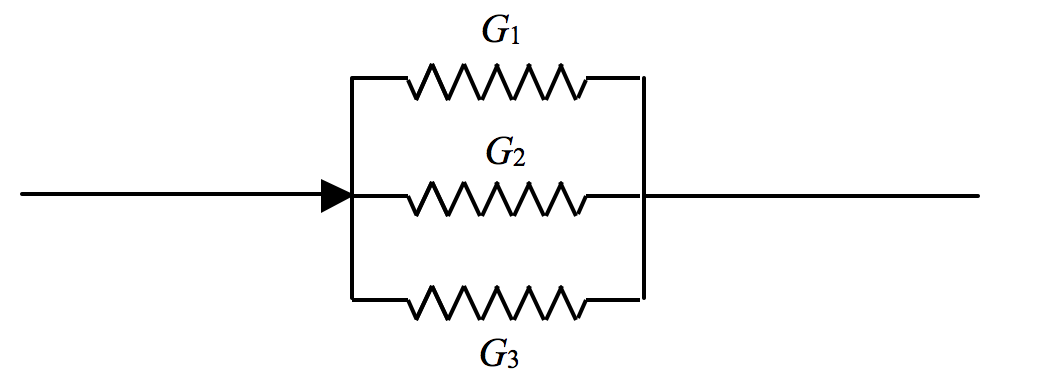
FIGURE IV.3
G=G1+G2+G3.
That is to say 1R=1R1+1R2+1R3.
The potential difference is the same across each. The current is greatest through the largest conductance – i.e. through the smallest resistance.


