2.3: Scalars and Vectors
- Page ID
- 68709
Vectors are essential to physics and engineering. Many fundamental physical quantities are vectors, including displacement, velocity, force, and electric and magnetic vector fields. Scalar products of vectors define other fundamental scalar physical quantities, such as energy. Vector products of vectors define still other fundamental vector physical quantities, such as torque and angular momentum. In other words, vectors are a component part of physics in much the same way as sentences are a component part of literature.

In introductory physics, vectors are Euclidean quantities that have geometric representations as arrows in one dimension (in a line), in two dimensions (in a plane), or in three dimensions (in space). They can be added, subtracted, or multiplied.
- Describe the difference between vector and scalar quantities.
- Identify the magnitude and direction of a vector.
- Explain the effect of multiplying a vector quantity by a scalar.
- Describe how one-dimensional vector quantities are added or subtracted.
- Explain the geometric construction for the addition or subtraction of vectors in a plane.
- Distinguish between a vector equation and a scalar equation.
Many familiar physical quantities can be specified completely by giving a single number and the appropriate unit. For example, “a class period lasts 50 min” or “the gas tank in my car holds 65 L” or “the distance between two posts is 100 m.” A physical quantity that can be specified completely in this manner is called a scalar quantity. Scalar is a synonym of “number.” Time, mass, distance, length, volume, temperature, and energy are examples of scalar quantities.
Scalar quantities that have the same physical units can be added or subtracted according to the usual rules of algebra for numbers. For example, a class ending 10 min earlier than 50 min lasts 50 min − 10 min = 40 min. Similarly, a 60-cal serving of corn followed by a 200-cal serving of donuts gives 60 cal + 200 cal = 260 cal of energy. When we multiply a scalar quantity by a number, we obtain the same scalar quantity but with a larger (or smaller) value. For example, if yesterday’s breakfast had 200 cal of energy and today’s breakfast has four times as much energy as it had yesterday, then today’s breakfast has 4(200 cal) = 800 cal of energy. Two scalar quantities can also be multiplied or divided by each other to form a derived scalar quantity. For example, if a train covers a distance of 100 km in 1.0 h, its speed is 100.0 km/1.0 h = 27.8 m/s, where the speed is a derived scalar quantity obtained by dividing distance by time.
Many physical quantities, however, cannot be described completely by just a single number of physical units. For example, when the U.S. Coast Guard dispatches a ship or a helicopter for a rescue mission, the rescue team must know not only the distance to the distress signal, but also the direction from which the signal is coming so they can get to its origin as quickly as possible. Physical quantities specified completely by giving a number of units (magnitude) and a direction are called vector quantities. Examples of vector quantities include displacement, velocity, position, force, and torque. In the language of mathematics, physical vector quantities are represented by mathematical objects called vectors (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). We can add or subtract two vectors, and we can multiply a vector by a scalar or by another vector, but we cannot divide by a vector. The operation of division by a vector is not defined.
Let’s examine vector algebra using a graphical method to be aware of basic terms and to develop a qualitative understanding. In practice, however, when it comes to solving physics problems, we use analytical methods. Analytical methods are more simple computationally and more accurate than graphical methods. From now on, to distinguish between a vector and a scalar quantity, we adopt the common convention that a letter with an arrow above it denotes a vector, and a letter without an arrow denotes a scalar. For example, a distance of 2.0 km, which is a scalar quantity, is denoted by d = 2.0 km, whereas a displacement of 2.0 km in some direction, which is a vector quantity, is denoted by \(\vec{d}\).
Suppose you tell a friend on a camping trip that you have discovered a terrific fishing hole 6 km from your tent. It is unlikely your friend would be able to find the hole easily unless you also communicate the direction in which it can be found with respect to your campsite. You may say, for example, “Walk about 6 km northeast from my tent.” The key concept here is that you have to give not one but two pieces of information—namely, the distance or magnitude (6 km) and the direction (northeast).
Displacement is a general term used to describe a change in position, such as during a trip from the tent to the fishing hole. Displacement is an example of a vector quantity. If you walk from the tent (location A) to the hole (location B), as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\), the vector \(\vec{D}\), representing your displacement, is drawn as the arrow that originates at point A and ends at point B. The arrowhead marks the end of the vector. The direction of the displacement vector \(\vec{D}\) is the direction of the arrow. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude (or size) D of vector \(\vec{D}\). Here, D = 6 km. Since the magnitude of a vector is its length, which is a positive number, the magnitude is also indicated by placing the absolute value notation around the symbol that denotes the vector; so, we can write equivalently that D ≡ |\(\vec{D}\)|. To solve a vector problem graphically, we need to draw the vector \(\vec{D}\) to scale. For example, if we assume 1 unit of distance (1 km) is represented in the drawing by a line segment of length u = 2 cm, then the total displacement in this example is represented by a vector of length d = 6u = 6(2 cm) = 12 cm , as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). Notice that here, to avoid confusion, we used D = 6 km to denote the magnitude of the actual displacement and d = 12 cm to denote the length of its representation in the drawing.
Suppose your friend walks from the campsite at A to the fishing pond at B and then walks back: from the fishing pond at B to the campsite at A. The magnitude of the displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) from A to B is the same as the magnitude of the displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{BA}\) from B to A (it equals 6 km in both cases), so we can write \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) = \(\vec{D}_{BA}\). However, vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) is not equal to vector \(\vec{D}_{BA}\) because these two vectors have different directions: \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) ≠ \(\vec{D}_{BA}\). In Figure 2.3, vector \(\vec{D}_{BA}\) would be represented by a vector with an origin at point B and an end at point A, indicating vector \(\vec{D}_{BA}\) points to the southwest, which is exactly 180° opposite to the direction of vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). We say that vector \(\vec{D}_{BA}\) is antiparallel to vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) and write \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) = \(-\vec{D}_{BA}\), where the minus sign indicates the antiparallel direction.
Two vectors that have identical directions are said to be parallel vectors—meaning, they are parallel to each other. Two parallel vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\) are equal, denoted by \(\vec{A}\) = \(\vec{B}\), if and only if they have equal magnitudes |\(\vec{A}\)| = |\(\vec{B}\)|. Two vectors with directions perpendicular to each other are said to be orthogonal vectors. These relations between vectors are illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).
Algebra of Vectors in One Dimension
Vectors can be multiplied by scalars, added to other vectors, or subtracted from other vectors. We can illustrate these vector concepts using an example of the fishing trip seen in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\).
Suppose your friend departs from point A (the campsite) and walks in the direction to point B (the fishing pond), but, along the way, stops to rest at some point C located three-quarters of the distance between A and B, beginning from point A (Figure \(\PageIndex{5a}\)). What is his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AC}\) when he reaches point C? We know that if he walks all the way to B, his displacement vector relative to A is \(\vec{D}_{AB}\), which has magnitude DAB = 6 km and a direction of northeast. If he walks only a 0.75 fraction of the total distance, maintaining the northeasterly direction, at point C he must be 0.75 DAB = 4.5 km away from the campsite at A. So, his displacement vector at the rest point C has magnitude DAC = 4.5 km = 0.75 DAB and is parallel to the displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). All of this can be stated succinctly in the form of the following vector equation:
\[\vec{D}_{AC} = 0.75\; \vec{D}_{AB} \ldotp \nonumber\]
In a vector equation, both sides of the equation are vectors. The previous equation is an example of a vector multiplied by a positive scalar (number) \(\alpha\) = 0.75. The result, \(\vec{D}_{AC}\), of such a multiplication is a new vector with a direction parallel to the direction of the original vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). In general, when a vector \(\vec{D}_{A}\) is multiplied by a positive scalar \(\alpha\), the result is a new vector \(\vec{D}_{B}\) that is parallel to \(\vec{D}_{A}\):
\[\vec{B} = \alpha \vec{A} \label{2.1}\]
The magnitude |\(\vec{B}\)| of this new vector is obtained by multiplying the magnitude |\(\vec{A}\)| of the original vector, as expressed by the scalar equation:
\[ B = | \alpha | A \ldotp \label{2.2}\]
In a scalar equation, both sides of the equation are numbers. Equation \ref{2.2} is a scalar equation because the magnitudes of vectors are scalar quantities (and positive numbers). If the scalar \(\alpha\) is negative in the vector equation Equation \ref{2.1}, then the magnitude |\(\vec{B}\)| of the new vector is still given by Equation \ref{2.2}, but the direction of the new vector \(\vec{B}\) is antiparallel to the direction of \(\vec{A}\). These principles are illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{6a}\) by two examples where the length of vector \(\vec{A}\) is 1.5 units. When \(\alpha\) = 2, the new vector \(\vec{B}\) = 2\(\vec{A}\) has length B = 2A = 3.0 units (twice as long as the original vector) and is parallel to the original vector. When \(\alpha\) = −2, the new vector \(\vec{C}\) = −2\(\vec{A}\) has length C = |−2| A = 3.0 units (twice as long as the original vector) and is antiparallel to the original vector.
Now suppose your fishing buddy departs from point A (the campsite), walking in the direction to point B (the fishing hole), but he realizes he lost his tackle box when he stopped to rest at point C (located three-quarters of the distance between A and B, beginning from point A). So, he turns back and retraces his steps in the direction toward the campsite and finds the box lying on the path at some point D only 1.2 km away from point C (see Figure \(\PageIndex{5b}\)). What is his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AD}\) when he finds the box at point D? What is his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{DB}\) from point D to the hole? We have already established that at rest point C his displacement vector is \(\vec{D}_{AC}\) = 0.75 \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). Starting at point C, he walks southwest (toward the campsite), which means his new displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{CD}\) from point C to point D is antiparallel to \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). Its magnitude |\(\vec{D}_{CD}\)| is DCD = 1.2 km = 0.2 DAB, so his second displacement vector is \(\vec{D}_{CD}\) = −0.2 \(\vec{D}_{AB}\). His total displacement \(\vec{D}_{AD}\) relative to the campsite is the vector sum of the two displacement vectors: vector \(\vec{D}_{AC}\) (from the campsite to the rest point) and vector \(\vec{D}_{CD}\) (from the rest point to the point where he finds his box):
\[\vec{D}_{AD} = \vec{D}_{AC} + \vec{D}_{CD} \ldotp \label{2.3}\]
The vector sum of two (or more vectors is called the resultant vector or, for short, the resultant. When the vectors on the right-hand-side of Equation \ref{2.3} are known, we can find the resultant \(\vec{D}_{AD}\) as follows:
\[\vec{D}_{AD} = \vec{D}_{AC} + \vec{D}_{CD} = 0.75\; \vec{D}_{AB} - 0.2\; \vec{D}_{AB} = (0.75 - 0.2) \vec{D}_{AB} = 0.55 \vec{D}_{AB} \ldotp \label{2.4}\]
When your friend finally reaches the pond at B, his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) from point A is the vector sum of his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{AD}\) from point A to point D and his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{DB}\) from point D to the fishing hole: \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) = \(\vec{D}_{AD}\) + \(\vec{D}_{DB}\) (see Figure \(\PageIndex{5c}\)). This means his displacement vector \(\vec{D}_{DB}\) is the difference of two vectors:
\[\vec{D}_{DB} = \vec{D}_{AB} − \vec{D}_{AD} = \vec{D}_{AB} + (− \vec{D}_{AD}) \ldotp \label{2.5}\]
Notice that a difference of two vectors is nothing more than a vector sum of two vectors because the second term in Equation \ref{2.5} is vector \(- \vec{D}_{AD}\) (which is antiparallel to \(\vec{D}_{AD}\)). When we substitute Equation \ref{2.4} into Equation \ref{2.5}, we obtain the second displacement vector:
\[\vec{D}_{DB} = \vec{D}_{AB} − \vec{D}_{AD} = \vec{D}_{AB} − 0.55\; \vec{D}_{AB} = (1.0 − 0.55)\; \vec{D}_{AB} = 0.45\; \vec{D}_{AB} \ldotp \label{2.6}\]
This result means your friend walked DDB = 0.45 DAB = 0.45(6.0 km) = 2.7 km from the point where he finds his tackle box to the fishing hole.
When vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\) lie along a line (that is, in one dimension), such as in the camping example, their resultant \(\vec{R}\) = \(\vec{A}\) + \(\vec{B}\) and their difference \(\vec{D}\) = \(\vec{A}\) − \(\vec{B}\) both lie along the same direction. We can illustrate the addition or subtraction of vectors by drawing the corresponding vectors to scale in one dimension, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\).
To illustrate the resultant when \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\) are two parallel vectors, we draw them along one line by placing the origin of one vector at the end of the other vector in head-to-tail fashion (see Figure (\PageIndex{6b}\)). The magnitude of this resultant is the sum of their magnitudes: R = A + B. The direction of the resultant is parallel to both vectors. When vector \(\vec{A}\) is antiparallel to vector \(\vec{B}\), we draw them along one line in either head-to-head fashion (Figure (\PageIndex{6c}\)) or tail-to-tail fashion. The magnitude of the vector difference, then, is the absolute value D = |A − B| of the difference of their magnitudes. The direction of the difference vector \(\vec{D}\) is parallel to the direction of the longer vector.
In general, in one dimension—as well as in higher dimensions, such as in a plane or in space—we can add any number of vectors and we can do so in any order because the addition of vectors is commutative,
\[\vec{A} + \vec{B} = \vec{B} + \vec{A} \ldotp \label{2.7}\]
and associative,
\[ (\vec{A} + \vec{B}) + \vec{C} = \vec{A} + (\vec{B} + \vec{C}) \ldotp \label{2.8}\]
Moreover, multiplication by a scalar is distributive:
\[ \alpha_{1} \vec{A} + \alpha_{2} \vec{A} = (\alpha_{1} + \alpha_{2}) \vec{A} \ldotp \label{2.9}\]
We used the distributive property in Equation \ref{2.4} and Equation \ref{2.6}.
When adding many vectors in one dimension, it is convenient to use the concept of a unit vector. A unit vector, which is denoted by a letter symbol with a hat, such as \(\hat{u}\), has a magnitude of one and does not have any physical unit so that |\(\hat{u}\)| ≡ u = 1. The only role of a unit vector is to specify direction. For example, instead of saying vector \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) has a magnitude of 6.0 km and a direction of northeast, we can introduce a unit vector \(\hat{u}\) that points to the northeast and say succinctly that \(\vec{D}_{AB}\) = (6.0 km) \(\hat{u}\). Then the southwesterly direction is simply given by the unit vector\(- \hat{u}\). In this way, the displacement of 6.0 km in the southwesterly direction is expressed by the vector
\[\vec{D}_{BA} = (−6.0\; km)\; \hat{u} \ldotp \nonumber\]
A long measuring stick rests against a wall in a physics laboratory with its 200-cm end at the floor. A ladybug lands on the 100-cm mark and crawls randomly along the stick. It first walks 15 cm toward the floor, then it walks 56 cm toward the wall, then it walks 3 cm toward the floor again. Then, after a brief stop, it continues for 25 cm toward the floor and then, again, it crawls up 19 cm toward the wall before coming to a complete rest (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Find the vector of its total displacement and its final resting position on the stick.
- Strategy
- If we choose the direction along the stick toward the floor as the direction of unit vector \(\hat{u}\), then the direction toward the floor is \(+ \hat{u}\) and the direction toward the wall is \(−\hat{u}\). The ladybug makes a total of five displacements:
\[ \begin{align*} \vec{D}_{1} &= (15\; cm)( + \hat{u}), \\[4pt] \vec{D}_{2} &= (56\; cm)( - \hat{u}), \\[4pt] \vec{D}_{3} &= (3\; cm)( + \hat{u}), \\[4pt] \vec{D}_{4} &= (25\; cm)( + \hat{u}), \; and \\[4pt] \vec{D}_{5} &= (19\; cm)( - \hat{u}) \ldotp \end{align*}\]
The total displacement \(\vec{D}\) is the resultant of all its displacement vectors.
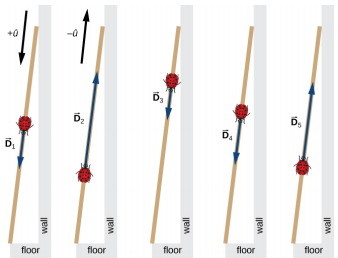
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Five displacements of the ladybug. Note that in this schematic drawing, magnitudes of displacements are not drawn to scale. (credit: modification of work by “Persian Poet Gal”/Wikimedia Commons) - Solution
-
The resultant of all the displacement vectors is
\[ \begin{align*} \vec{D} &= \vec{D}_{1} + \vec{D}_{2} + \vec{D}_{3} + \vec{D}_{4} + \vec{D}_{5} \\[4pt] &= (15\; cm)( + \hat{u} ) + (56\; cm)( −\hat{u} ) + (3\; cm)( + \hat{u} ) + (25\; cm)( + \hat{u}) + (19\; cm)( − \hat{u}) \\[4pt] &= (15 − 56 + 3 + 25 − 19) cm\; \hat{u} \\[4pt] &= −32\; cm\; \hat{u} \ldotp \end{align*}\]
In this calculation, we use the distributive law given by Equation 2.2.9. The result reads that the total displacement vector points away from the 100-cm mark (initial landing site) toward the end of the meter stick that touches the wall. The end that touches the wall is marked 0 cm, so the final position of the ladybug is at the (100 – 32) cm = 68-cm mark.
Algebra of Vectors in Two Dimensions
When vectors lie in a plane—that is, when they are in two dimensions—they can be multiplied by scalars, added to other vectors, or subtracted from other vectors in accordance with the general laws expressed by Equation 2.2.1, Equation 2..2.2, Equation 2.2.7, and Equation 2.2.8. However, the addition rule for two vectors in a plane becomes more complicated than the rule for vector addition in one dimension. We have to use the laws of geometry to construct resultant vectors, followed by trigonometry to find vector magnitudes and directions. This geometric approach is commonly used in navigation (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). In this section, we need to have at hand two rulers, a triangle, a protractor, a pencil, and an eraser for drawing vectors to scale by geometric constructions.
For a geometric construction of the sum of two vectors in a plane, we follow the parallelogram rule. Suppose two vectors \(\vec{A}\) and \(\vec{B}\) are at the arbitrary positions shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). Translate either one of them in parallel to the beginning of the other vector, so that after the translation, both vectors have their origins at the same point. Now, at the end of vector \(\vec{A}\) we draw a line parallel to vector \(\vec{B}\) and at the end of vector \(\vec{B}\) we draw a line parallel to vector \(\vec{A}\) (the dashed lines in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). In this way, we obtain a parallelogram. From the origin of the two vectors we draw a diagonal that is the resultant \(\vec{R}\) of the two vectors: \(\vec{R}\) = \(\vec{A}\) + \(\vec{B}\) (Figure \(\PageIndex{3a}\)). The other diagonal of this parallelogram is the vector difference of the two vectors \(\vec{D}\) = \(\vec{A}\) − \(\vec{B}\), as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3b}\). Notice that the end of the difference vector is placed at the end of vector \(\vec{A}\).
It follows from the parallelogram rule that neither the magnitude of the resultant vector nor the magnitude of the difference vector can be expressed as a simple sum or difference of magnitudes A and B, because the length of a diagonal cannot be expressed as a simple sum of side lengths. When using a geometric construction to find magnitudes |\(\vec{R}\)| and |\(\vec{D}\)|, we have to use trigonometry laws for triangles, which may lead to complicated algebra. There are two ways to circumvent this algebraic complexity. One way is to use the method of components, which we examine in the next section. The other way is to draw the vectors to scale, as is done in navigation, and read approximate vector lengths and angles (directions) from the graphs. In this section we examine the second approach.
If we need to add three or more vectors, we repeat the parallelogram rule for the pairs of vectors until we find the resultant of all of the resultants. For three vectors, for example, we first find the resultant of vector 1 and vector 2, and then we find the resultant of this resultant and vector 3. The order in which we select the pairs of vectors does not matter because the operation of vector addition is commutative and associative (see Equation 2.2.7 and Equation 2.2.8). Before we state a general rule that follows from repetitive applications of the parallelogram rule, let’s look at the following example.
Suppose you plan a vacation trip in Florida. Departing from Tallahassee, the state capital, you plan to visit your uncle Joe in Jacksonville, see your cousin Vinny in Daytona Beach, stop for a little fun in Orlando, see a circus performance in Tampa, and visit the University of Florida in Gainesville. Your route may be represented by five displacement vectors \(\vec{A}\), \(\vec{B}\), \(\vec{C}\), \(\vec{D}\), and \(\vec{E}\), which are indicated by the red vectors in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). What is your total displacement when you reach Gainesville? The total displacement is the vector sum of all five displacement vectors, which may be found by using the parallelogram rule four times. Alternatively, recall that the displacement vector has its beginning at the initial position (Tallahassee) and its end at the final position (Gainesville), so the total displacement vector can be drawn directly as an arrow connecting Tallahassee with Gainesville (see the green vector in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). When we use the parallelogram rule four times, the resultant \(\vec{R}\) we obtain is exactly this green vector connecting Tallahassee with Gainesville: \(\vec{R}\) = \(\vec{A}\) + \(\vec{B}\) + \(\vec{C}\) + \(\vec{D}\) + \(\vec{E}\).
Drawing the resultant vector of many vectors can be generalized by using the following tail-to-head geometric construction. Suppose we want to draw the resultant vector \(\vec{R}\) of four vectors \(\vec{A}\), \(\vec{B}\), \(\vec{C}\), and \(\vec{D}\) (Figure \(\PageIndex{5a}\)). We select any one of the vectors as the first vector and make a parallel translation of a second vector to a position where the origin (“tail”) of the second vector coincides with the end (“head”) of the first vector. Then, we select a third vector and make a parallel translation of the third vector to a position where the origin of the third vector coincides with the end of the second vector. We repeat this procedure until all the vectors are in a head-to-tail arrangement like the one shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). We draw the resultant vector \(\vec{R}\) by connecting the origin (“tail”) of the first vector with the end (“head”) of the last vector. The end of the resultant vector is at the end of the last vector. Because the addition of vectors is associative and commutative, we obtain the same resultant vector regardless of which vector we choose to be first, second, third, or fourth in this construction.
The three displacement vectors \(\vec{A}\), \(\vec{B}\), and \(\vec{C}\) in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) are specified by their magnitudes A = 10.0, B = 7.0, and C = 8.0, respectively, and by their respective direction angles with the horizontal direction \(\alpha\) = 35°, \(\beta\) = −110°, and \(\gamma\) = 30°. The physical units of the magnitudes are centimeters. Choose a convenient scale and use a ruler and a protractor to find the following vector sums: (a) \(\vec{R}\) = \(\vec{A}\) + \(\vec{B}\), (b) \(\vec{D}\) = \(\vec{A}\) − \(\vec{B}\), and (c) \(\vec{S}\) = \(\vec{A}\) − \(3 \vec{B}\) + \(\vec{C}\).
- Strategy
-
In geometric construction, to find a vector means to find its magnitude and its direction angle with the horizontal direction. The strategy is to draw to scale the vectors that appear on the right-hand side of the equation and construct the resultant vector. Then, use a ruler and a protractor to read the magnitude of the resultant and the direction angle. For parts (a) and (b) we use the parallelogram rule. For (c) we use the tail-to-head method.
- Solution
-
For parts (a) and (b), we attach the origin of vector \(\vec{B}\) to the origin of vector \(\vec{A}\), as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\), and construct a parallelogram. The shorter diagonal of this parallelogram is the sum \(\vec{A}\) + \(\vec{B}\). The longer of the diagonals is the difference \(\vec{A}\) − \(\vec{B}\). We use a ruler to measure the lengths of the diagonals, and a protractor to measure the angles with the horizontal. For the resultant \(\vec{R}\), we obtain R = 5.8 cm and \(\theta_{R}\) ≈ 0°. For the difference \(\vec{D}\), we obtain D = 16.2 cm and \(\theta_{D}\) = 49.3°, which are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\).
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): Using the parallelogram rule to solve (a) (finding the resultant, red) and (b) (finding the difference, blue). For (c), we can start with vector −3 \(\vec{B}\) and draw the remaining vectors tail-to-head as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\). In vector addition, the order in which we draw the vectors is unimportant, but drawing the vectors to scale is very important. Next, we draw vector \(\vec{S}\) from the origin of the first vector to the end of the last vector and place the arrowhead at the end of \(\vec{S}\). We use a ruler to measure the length of \(\vec{S}\), and find that its magnitude is S = 36.9 cm. We use a protractor and find that its direction angle is \(\theta_{S}\) = 52.9°. This solution is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\).
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\): Using the tail-to-head method to solve (c) (finding vector \(\vec{S}\), green).


