7.8: Moving-coil Ammeter
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
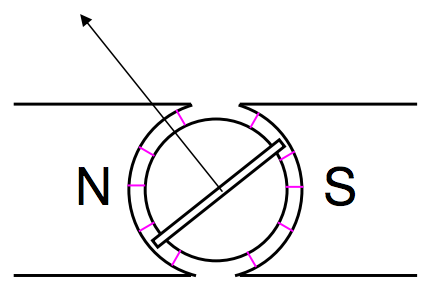
FIGURE VII.5
The current is led into the coil of N turns through a spiral spring of torsion constant c. The coil is between two poles of a specially-shaped magnet, and there is an iron cylinder inside the coil. This ensures that the magnetic field is everywhere parallel to the plane of the coil; that is, at right angles to its magnetic moment vector. This ensures that the deflection of the coil increases linearly with current, for there is no sinθ factor. When a current flows through the coil, the torque on it is NABI, and this in counteracted by the torque cθ of the holding springs. Thus the current and deflection are related by
NABI=cθ.


