2.A: Vectors (Answers)
- Page ID
- 10315
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Check Your Understanding
2.1. a. not equal because they are orthogonal;
b. not equal because they have different magnitudes;
c. not equal because they have different magnitudes and directions;
d. not equal because they are antiparallel;
e. equal.
2.2. 16 m; \(\vec{D}=−16m\hat{u}\)
2.3. G = 28.2 cm, \(θ_G=291°\)
2.4. \(\vec{D}=(−5.0\hat{i}−3.0\hat{j})cm\); the fly moved 5.0 cm to the left and 3.0 cm down from its landing site.
2.5. 5.83 cm, \(211°\)
2.6. \(\vec{D}=(−20m)\hat{j}\)
2.7. 35.1 m/s = 126.4 km/h
2.8. \(\vec{G}=(10.25\hat{i}−26.22\hat{j})cm\)
2.9. D = 55.7 N; direction \(65.7°\) north of east
2.10. \(\hat{v}=0.8\hat{i}+0.6\hat{j}, 36.87°\) north of east
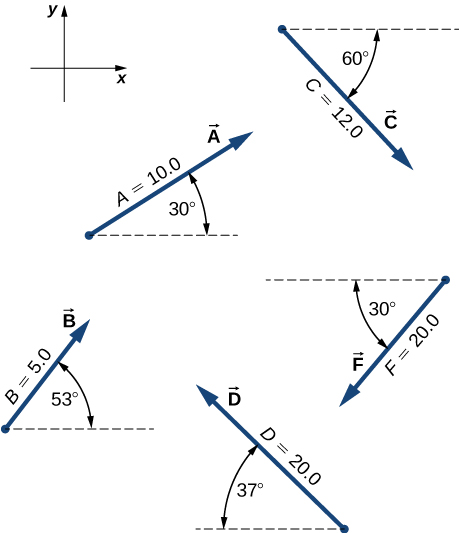
2.11. \(\vec{A}⋅\vec{B}=−57.3, \vec{F}⋅\vec{C}=27.8\)
2.13. \(131.9°\)
2.14. \(W_1=1.5J, W_2=0.3J\)
2.15. \(\vec{A}×\vec{B}=−40.1\hat{k}\) or, equivalently, \(∣\vec{A}×\vec{B}∣=40.1\), and the direction is into the page; \(\vec{C}×\vec{F}=+157.6\hat{k}\) or, equivalently, \(∣\vec{C}×\vec{F}∣=157.6\), and the direction is out of the page.
2.16. a. \(−2\hat{k}\),
b. 2,
c. \(153.4°\),
d. \(135°\)
Conceptual Questions
1. scalar
3. answers may vary
5. parallel, sum of magnitudes, antiparallel, zero
7. no, yes
9. zero, yes
11. no
13. equal, equal, the same
15. a unit vector of the x-axis
17. They are equal.
19. yes
21. a. \(C=\vec{A}⋅\vec{B}\)
b. \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}·\vec{B}\) or \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}−\vec{B}\)
c. \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}×\vec{B}\),
d. \(\vec{C}=A\vec{B}\),
e. \(\vec{C}+2\vec{A}=\vec{B}\),
f. \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}×\vec{B}\),
g. left side is a scalar and right side is a vector,
h. \(\vec{C}=2\vec{A}×\vec{B}\),
i. \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}/B\),
j. \(\vec{C}=\vec{A}/B\)
23. They are orthogonal.
Problems
25. \(\vec{h}=−49m\hat{u}\), 49 m
27. 30.8 m, \(35.7°\) west of north
29. 134 km, \(80°\)
31. 7.34 km, \(63.5°\) south of east
33. 3.8 km east, 3.2 km north, 7.0 km
35. 14.3 km, \(65°\)
37. a. \(\vec{A}=+8.66\hat{i}+5.00\hat{j}\),
b. \(\vec{B}=+3.01\hat{i}+3.99\hat{j}\),
c. \(\vec{C}=+6.00\hat{i}−10.39\hat{j}\),
d. \(\vec{D⃗}=−15.97\hat{i}+12.04\hat{j}\),
f. \(\vec{F}=−17.32\hat{i}−10.00\hat{j}\)
39. a. 1.94 km, 7.24 km;
b. proof
41. 3.8 km east, 3.2 km north, 2.0 km, \(\vec{D}=(3.8\hat{i}+3.2\hat{j})km
43. \(P_1(2.165m,1.250m), P_2(−1.900m,3.290m), 5.27 m\)
45. 8.60 m, \(A(2\sqrt{5}m,0.647π), B(3\sqrt{2}m,0.75π)\)
47. a. \(\vec{A}+\vec{B}=−4\hat{i}−6\hat{j}\), \( |\vec{A}+\vec{B}∣=7.211,θ=236.3°\);
b. \(\vec{A}−\vec{B}=-2\hat{i}+2\hat{j}, ∣\vec{A}−\vec{B}∣=2\sqrt{2},θ=135°\)
49. a. \(\vec{C}=(5.0\hat{i}−1.0\hat{j}−3.0\hat{k})m,C=5.92m\);
b. \(\vec{D}=(4.0\hat{i}−11.0\hat{j}+15.0\hat{k})m,D=19.03m\).
51. \(\vec{D}=(3.3\hat{i}−6.6\hat{j})km, \hat{i} is to the east, 7.34 km, −63.5°\)
53. a.\(\vec{R}=−1.35\hat{i}−22.04\hat{j}\),
b. \(\vec{R}=−17.98\hat{i}+0.89\hat{j}\)
55. \(\vec{D}=(200\hat{i}+300\hat{j})yd\), D = 360.5 yd, \(56.3°\) north of east; The numerical answers would stay the same but the physical unit would be meters. The physical meaning and distances would be about the same because 1 yd is comparable with 1 m.
57. \(\vec{R}=−3\hat{i}−16\hat{j}\)
59. \(\vec{E⃗}=E\hat{E}, E_x=+178.9V/m, E_y=−357.8V/m, E_z=0.0V/m, θ_E=−tan^{−1}(2)\)
61. a. \(\vec{R}_B=(12.278\hat{i}+7.089\hat{j}+2.500\hat{k})km, \(\vec{R}_D=(−0.262\hat{i}+3.000\hat{k})km\);
b. \(∣\vec{R}_B−\vec{R}_D∣=14.414km\)|R→B−R→D|=14.414km
63. a. 8.66,
b. 10.39,
c. 0.866,
d. 17.32
65. \(θ_i=64.12°,θ_j=150.79°,θ_k=77.39°\)
67. a. \(−119.98\hat{k}\)
b. \(0\hat{k}\),
c. \(+93.69\hat{k}\),
d. \(−240.0\hat{k}\),
e. \(+3.993\hat{k}\),
f. \(−3.009\hat{k}\),
g. \(+14.99\hat{k}\),
h. 0
69. a. 0,
b. 173,194,
c. +199,993\(\hat{k}\)
Additional Problems
71. a. 18.4 km and 26.2 km,
b. 31.5 km and 5.56 km
73. a. \((r,φ+π/2)\),
b. \((2r,φ+2π)(\),
c. \((3r,−φ)\)
75. \(d_{PM}=33.12nmi=61.34km,d_{NP}=35.47nmi=65.69km\)
77. proof
79. a. 10.00 m,
b. \(5πm\),
c. 0
81. 22.2 km/h, \(35.8°\). south of west
83. 240.2 m, \(2.2°\) south of west
85. \(\vec{B}=−4.0\hat{i}+3.0\hat{j}\) or \(\vec{B}=4.0\hat{i}−3.0\hat{j}\)
87. proof
Challenge Problems
89. \(G_{⊥}=2375\sqrt{17}≈9792\)
91. proof


