1.9.3: Finding Angle Measurements
- Page ID
- 72962
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Angles
Lines, line segments, points, and rays are the building blocks of other figures. For example, two rays with a common endpoint make up an angle. The common endpoint of the angle is called the vertex.
The angle ABC is shown below. This angle can also be called \(\angle\)ABC, \(\angle\)CBA or simply \(\angle\)B. When you are naming angles, be careful to include the vertex (here, point B) as the middle letter.

The image below shows a few angles on a plane. Notice that the label of each angle is written “point-vertex-point,” and the geometric notation is in the form \(\angle\)ABC.

Sometimes angles are very narrow; sometimes they are very wide. When people talk about the “size” of an angle, they are referring to the arc between the two rays. The length of the rays has nothing to do with the size of the angle itself. Drawings of angles will often include an arc (as shown above) to help the reader identify the correct ‘side’ of the angle.
Think about an analog clock face. The minute and hour hands are both fixed at a point in the middle of the clock. As time passes, the hands rotate around the fixed point, making larger and smaller angles as they go. The length of the hands does not impact the angle that is made by the hands.
An angle is measured in degrees, represented by the symbol º. A circle is defined as having 360º. (In skateboarding and basketball, “doing a 360” refers to jumping and doing one complete body rotation.
A right angle is any degree that measures exactly 90º. This represents exactly one-quarter of the way around a circle. Rectangles contain exactly four right angles. A corner mark is often used to denote a right angle, as shown in right angle DCB below.
Angles that are between 0º and 90º (smaller than right angles) are called acute angles. Angles that are between 90º and 180º (larger than right angles and less than 180º) are called obtuse angles. And an angle that measures exactly 180º is called a straight angle because it forms a straight line.

Label each angle below as acute, right, or obtuse.

- Solution
-
You can start by identifying any right angles.
\(\angle\)GFI is a right angle, as indicated by the corner mark at vertex F.
Acute angles will be smaller than \(\angle\)GFI (or less than 90º). This means that \(\angle\)DAB and \(\angle\)MLN are acute.
\(\angle\)TQS is larger than \(\angle\)GFI, so it is an obtuse angle.
Answer: \(\angle\)DAB and \(\angle\)MLN are acute angles. \(\angle\)GFI is a right angle. \(\angle\)TQS is an obtuse angle.
Identify each point, ray, and angle in the picture below.

- Solution
-
Begin by identifying each point in the figure. There are 4: E, F, G, and J.

Now find rays. A ray begins at one point, and then continues through another point towards infinity (indicated by an arrow). Three rays start at point J: \(\overrightarrow{JE}\), \(\overrightarrow{JF}\), and \(\overrightarrow{JG}\). But also notice that a ray could start at point F and go through J and G, and another could start at point G and go through J and F. These rays can be represented by \(\overrightarrow{GF}\) and \(\overrightarrow{FG}\).

Finally, look for angles. \(\angle\)EJG is obtuse, \(\angle\)EJF is acute, and \(\angle\)FJG is straight. (Don’t forget those straight angles!)

Answer: Points: E, F, G, J
Rays: \(\overrightarrow{JE}\), \(\overrightarrow{JG}\), \(\overrightarrow{JF}\), \(\overrightarrow{GF}\), \(\overrightarrow{FG}\)
Angles: \(\angle\)EJG, \(\angle\)EJF, \(\angle\)FJG
Identify the acute angles in the given image:

Finding Angle Measurements
Understanding how parallel and perpendicular lines relate can help you figure out the measurements of some unknown angles. To start, all you need to remember is that perpendicular lines intersect at a 90º angle and that a straight angle measures 180º.
The measure of an angle such as \(\angle\)A is written as m\(\angle\)A. Look at the example below. How can you find the measurements of the unmarked angles?
Find the measurement of \(\angle\)IJF.

- Solution
-
Only one angle, \(\angle\)HJM, is marked in the image. Notice that it is a right angle, so it measures 90º. \(\angle\)HJM is formed by the intersection of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{IM}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{HF}\). Since \(\overleftrightarrow{IM}\) is a line, \(\angle\)IJM is a straight angle measuring 180º.

You can use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)HJI :
m\(\angle\)HJM + m\(\angle\)HJI = m\(\angle\)IJM
90º + m\(\angle\)HJI = 180º
m\(\angle\)HJI = 90º

Now use the same logic to find the measurement of \(\angle\)IJF. \(\angle\)IJF is formed by the intersection of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{IM}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{HF}\). Since \(\overleftrightarrow{HF}\) is a line, \(\angle\)HJF will be a straight angle measuring 180º.

You know that \(\angle\)HJI measures 90º. Use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)IJF:
m\(\angle\)HJM + m\(\angle\)IJF = m\(\angle\)HJF
90º + m\(\angle\)IJF = 180º
m\(\angle\)IJF = 90º

Answer: m\(\angle\)IJF = 90º
In this example, you may have noticed that angles \(\angle\)HJI, \(\angle\)IJF, and \(\angle\)HJM are all right angles. (If you were asked to find the measurement of \(\angle\)FJM, you would find that angle to be 90º, too.) This is what happens when two lines are perpendicular—the four angles created by the intersection are all right angles.
Not all intersections happen at right angles, though. In the example below, notice how you can use the same technique as shown above (using straight angles) to find the measurement of a missing angle.
Find the measurement of \(\angle\)DAC.

- Solution
-
This image shows the line \(\overleftrightarrow{BC}\) and the ray \(\overrightarrow{AD}\) intersecting at point A. The measurement of \(\angle\)BAD is 135º. You can use straight angles to find the measurement of \(\angle\)DAC.

\(\angle\)BAC is a straight angle, so it measures 180º.

Use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)DAC.
m\(\angle\)BAD + m\(\angle\)DAC = m\(\angle\)BAC
135º + m\(\angle\)DAC = 180º
m\(\angle\)DAC = 45º

Answer: m\(\angle\)DAC = 45º

Find the measurement of \(\angle\)CAD.

Supplementary and Complementary Angles
In the example above, m\(\angle\)BAC and m\(\angle\)DAC add up to 180º. Two angles whose measures add up to 180º are called supplementary angles. There’s also a term for two angles whose measurements add up to 90º, they are called complementary angles.
One way to remember the difference between the two terms is that “corner” and “complementary” each begin with c (a 90º angle looks like a corner), while straight and “supplementary” each begin with s (a straight angle measures 180º).
If you can identify supplementary or complementary angles within a problem, finding missing angle measurements is often simply a matter of adding or subtracting.
Two angles are supplementary. If one of the angles measures 48º, what is the measurement of the other angle\(\angle\)
- Solution
-
Two supplementary angles make up a straight angle, so the measurements of the two angles will be 180º.
m\(\angle\)A + m\(\angle\)B = 180º
You know the measurement of one angle. To find the measurement of the second angle, subtract 48º from 180º.
48º+ m\(\angle\)B = 180º
m\(\angle\)B = 180º - 48º
m\(\angle\)B = 132º
Answer: The measurement of the other angle is 132º
Find the measurement of \(\angle\)AXZ.

- Solution
-
This image shows two intersecting lines, \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{YZ}\). They intersect at point X, forming four angles. Angles \(\angle\)AXY and \(\angle\)AXZ are supplementary because together they make up the straight angle \(\angle\)YXZ.

Use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)AXZ.
m\(\angle\)AXY + m\(\angle\)AXZ = m\(\angle\)YXZ
30º + m\(\angle\)AXZ = 180º
m\(\angle\)AXZ = 150º

Answer: m\(\angle\)AXZ = 150º
Find the measurement of \(\angle\)BAC.

- Solution
-
This image shows the line \(\overleftrightarrow{CF}\) and the rays \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{AD}\), all intersecting at point A. Angle \(\angle\)BAD is a right angle. Angles \(\angle\)BAC and \(\angle\)CAD are complementary because together they create \(\angle\)BAD.

Use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)BAC .
m\(\angle\)BAC + m\(\angle\)CAD = m\(\angle\)BAD
m\(\angle\)BAC + 50º = 90º
m\(\angle\)BAC = 40º

Answer: m\(\angle\)BAC = 40º
Find the measurement of \(\angle\)CAD.

- Solution
-
You know the measurements of two angles here: \(\angle\)CAB and \(\angle\)DAE. You also know that m\(\angle\)BAE = 180º.

Use this information to find the measurement of \(\angle\)CAD.
m\(\angle\)BAC + m\(\angle\)CAD + m\(\angle\)DAE = m\(\angle\)BAE
25º + m\(\angle\)CAD + 75º = 180º
m\(\angle\)CAD + 100º = 180º
m\(\angle\)CAD = 80º

Answer: m\(\angle\)CAD = 80º
Parallel and Transversal Lines
Two lines are parallel if they do not meet, no matter how far they are extended. The symbol for parallel is \(||\). In Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{A B}\) \(||\) \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{C D}\). The arrow marks are used to indicate the lines are parallel.



A transversal is a line that intersects two other lines at two distinct points. In Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), \(\overleftrightarrow{EF}\) is a transversal. \(\angle x\) and \(\angle x^{\prime}\) are called alternate interior angles of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\). The word "alternate," here, means that the angles are on different sides of the transversal, one angle formed with \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and the other formed with \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\). The word "interior" means that they are between the two lines. Notice that they form the letter "\(Z\)." (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). \(\angle y\) and \(\angle y^{\prime}\) are also alternate interior angles. They also form a "\(Z\)" though It is stretched out and backwards. Viewed from the side, the letter "\(Z\)" may also look like an "\(N\)."

Alternate interior angles are important because of the following theorem:
If two lines are parallel then their alternate interior angles are equal, If the alternate interior angles of two lines are equal then the lines must 'oe parallel,
In Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\), \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) must be parallel to \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\) because the alternate interior angles are both \(30^{\circ}\). Notice that the other pair of alternate interior angles, \(\angle y\) and \(\angle y'\), are also equal. They are both \(150^{\circ}\). In Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\), the lines are not parallel and none of the alternate interior angles are equal.


Find \(x, y\) and \(z\):

- Solution
-
\(\overleftrightarrow{AB} || \overleftrightarrow{CD}\) since the arrows indicate parallel lines. \(x^{\circ} = 40^{\circ}\) because alternate interior angles of parallel lines are equal. \(y^{\circ} = z^{\circ} = 180^{\circ} - 40^{\circ} = 140^{\circ}\).
Answer: \(x = 40, y = 140, z = 140\).
Corresponding angles of two lines are two angles which are on the same side of the two lines and the same side of the transversal, In Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\), \(\angle w\) and \(\angle w'\) are corresponding angles of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\). They form the letter "\(F\)." \(\angle x\) and \(\angle x'\), \(\angle y\) and \(\angle y'\), and \(\angle z\) and \(\angle z'\) are other pairs of corresponding angles of \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\). They all form the letter "\(F\)", though it might be a backwards or upside down "\(F\)" (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)).


Corresponding angles are important because of the following theorem:
If two lines are parallel then their corresponding angles are equal. If the corresponding angles of two lines are equal then the lines must be parallel.
Find \(x\):

- Solution
-
The arrow indicate \(\overleftrightarrow{AB} || \overleftrightarrow{CD}\). Therefore \(x^{\circ} = 110^{\circ}\) because \(x^{\circ}\) and \(110^{\circ}\) are the measures of corresponding angles of the parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\).
Answer: \(x = 110\).

Notice that we can now find all the other angles in Example \(PageIndex{2}\). Each one is either supplementary to one of the \(110^{\circ}\) angles or forms equal vertical angles with one of them (Figure \(PageIndex{10}\)). Therefore all the corresponding angles are equal, Also each pair of alternate interior angles is equal. It is not hard to see that if just one pair of corresponding angles or one pair of alternate interior angles are equal then so are all other pairs of corresponding and alternate interior angles.
Proof of Theorem \(\PageIndex{2}\): The corresponding angles will be equal if the alternate interior angles are equal and vice versa. Therefore Theorem \(\PageIndex{2}\) follows directly from Therorem \(\PageIndex{1}\).
In Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\), \(\angle x\) and \(\angle x'\) are called interior angles on the same side of the transversal.(In some textbooks, interior angles on the same sdie of the transversal are called cointerior angles.) \(\angle y\) and \(\angle y'\) are also interior angles on the same side of the transversal, Notice that each pair of angles forms the letter "\(C\)." Compare Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\) with Figure 10 and also with Example \(\PageIndex{1}\), The following theorem is then apparent:

If two lines are parallel then the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary (they add uP to \(180^{\circ}\)). If the interior angles of two lines on the same side of the transversal are supplementary then the lines must be parallel.
Find \(x\) and the marked angles:

- Solution
-
The lines are parallel so by Theorem \(\PageIndex{3}\) the two labelled angles must be supplementary.
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 2x + 30} & = & {180} \\ {3x + 30} & = & {180} \\ {3x} & = & {180 - 30} \\ {3x} & = & {150} \\ {x} & = & {50} \end{array}\]
\(\angle CHG = x = 50^{\circ}\)
\(\angle AGH = 2x + 30 = 2(50) + 30 = 100 + 30 = 130^{\circ}\).
Check:

Answer: \(x = 50\), \(\angle CHG = 50^{\circ}\), \(\angle AGHa = 130^{\circ}\).
Find \(x\) and the marked angles:

- Solution
-
\(\angle BEF = 3x + 40^{\circ}\) because vertical angles are equal. \(\angle BEF\) and \(\angle DFE\) are interior angles on the same side of the transversal, and therefore are supplementary because the lines are parallel.
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {3x + 40 + 2x + 50} & = & {180} \\ {5x + 90} & = & {180} \\ {5x} & = & {180 - 90} \\ {5x} & = & {90} \\ {x} & = & {18} \end{array}\]
\(\angle AEC = 3x + 40 = 3(18) + 40 = 54 + 40 = 94^{\circ}\)
\(\angle DFE = 2x + 50 = 2(18) + 50 = 36 + 50 = 86^{\circ}\)
Check:

Answer: \(x = 18\), \(\angle AEG = 94^{\circ}\), \(\angle DFE = 86^{\circ}\).
List all pairs of alternate interior angles in the diagram, (The single arrow indicates \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) is parallel to \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\) and the double arrow indicates \(\overleftrightarrow{AD}\) is parallel to \(\overleftrightarrow{BC}\).

- Solution
-
We see if a letter \(Z\) or \(N\) can be formed using the line segments in the diagram (Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)),

Answer: \(\angle DCA\) and \(\angle CAB\) are alternate interior angles of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CD}\). \(\angle DAC\) and \(\angle ACB\) are alternate interior angles of lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AD}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{BC}\)
A telescope is pointed at a star \(70^{\circ}\) above the horizon, What angle \(x^{\circ}\) must the mirror \(BD\) make with the horizontal so that the star can be seen in the eyepiece \(E\)?

- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Examples
Find the angle \(\alpha\) as a function of \(\theta\)
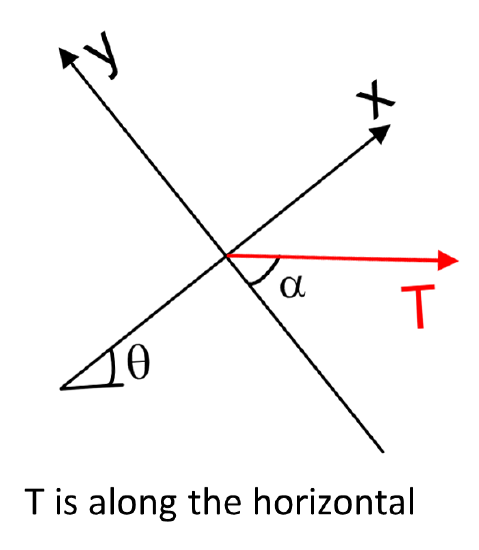
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
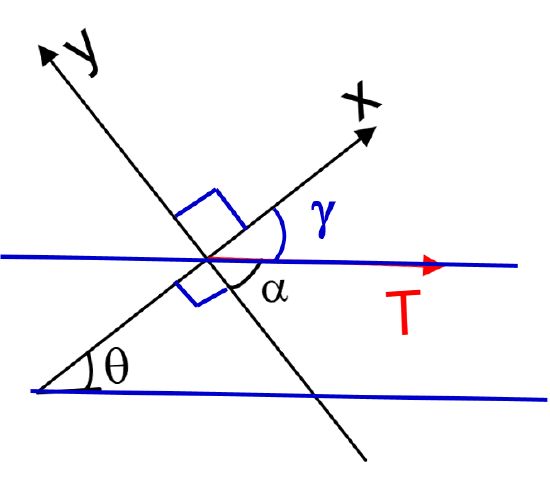
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
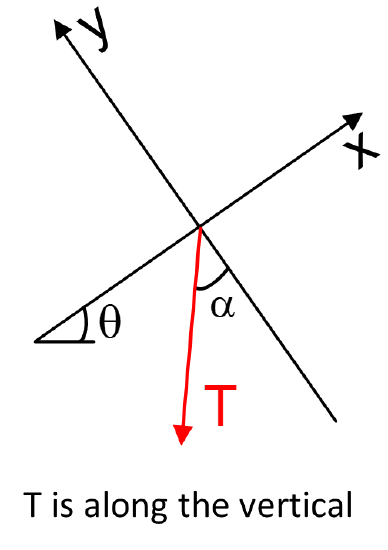
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
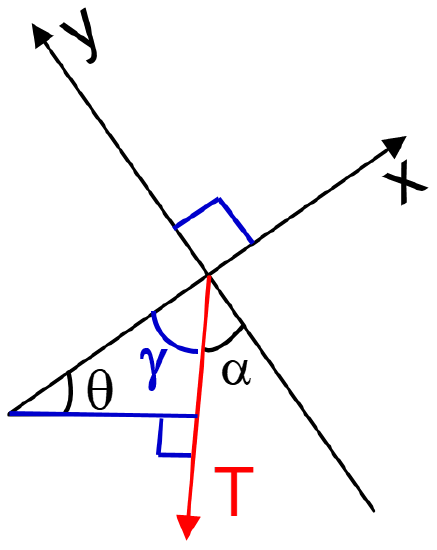
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)

- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
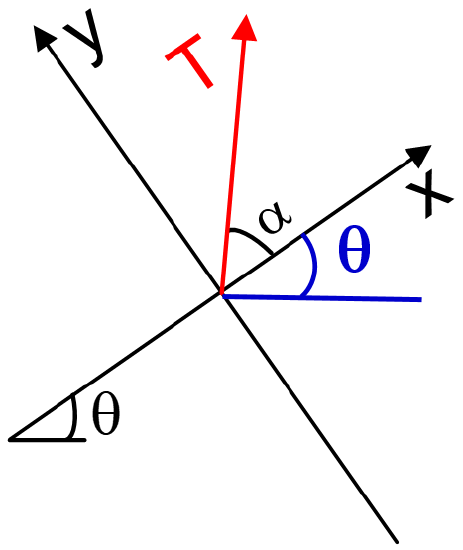
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
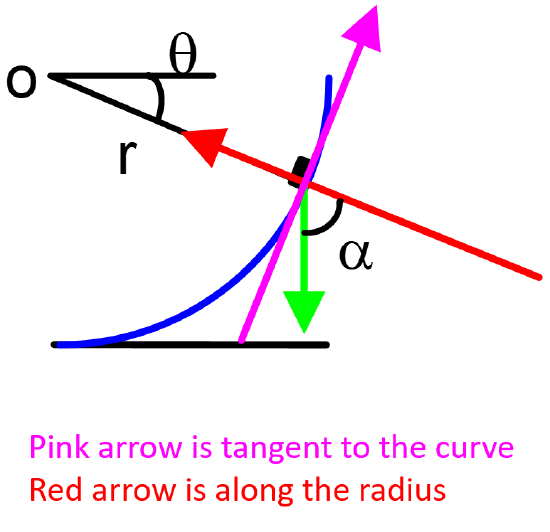
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
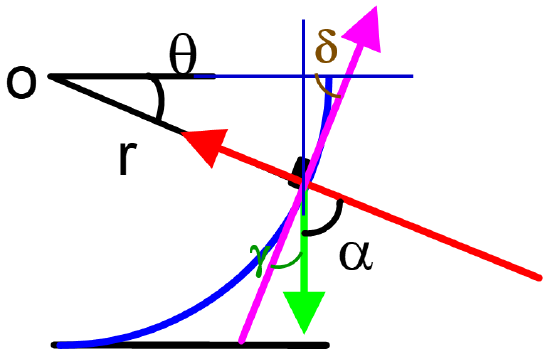
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
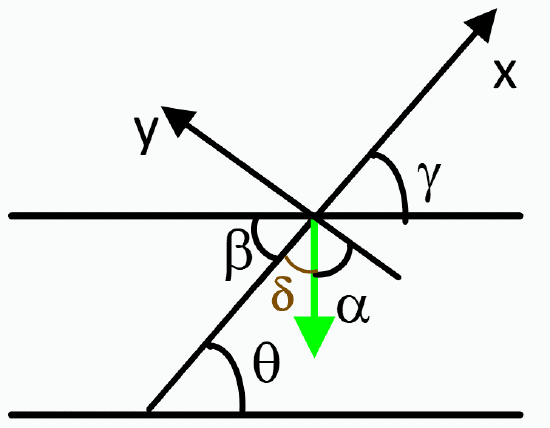
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)
Find the rest of the angles as a function of \(\theta\)
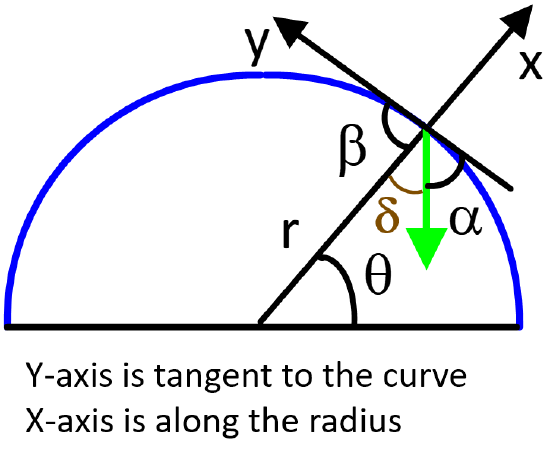
- Solution
-
\(x^{\circ} = \angle BCE\) because they are alternate interior angles of parallel lines \(\overleftrightarrow{AB}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{CE}\). \(\angle DCF = \angle BCE = x^{\circ}\) because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore
\[\begin{array} {rcl} {x + 70 + x} & = & {180} \\ {2x + 70} & = & {180} \\ {2x} & = & {110} \\ {x} & = & {55} \end{array}\]
Answer: \(55^{\circ}\)


