30.4: Ball with External Forces Rolling on Horizontal Plane
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
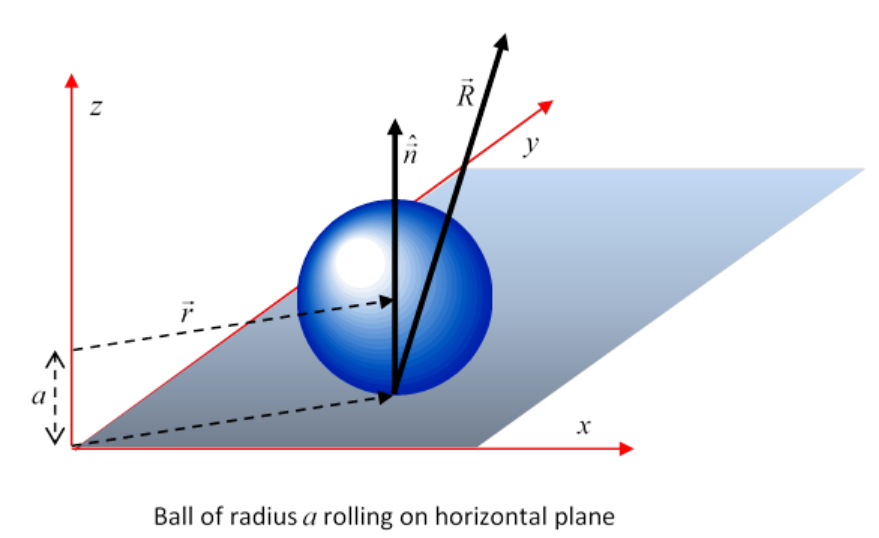
Here’s how it works for a simple example (done in Landau, and see diagram below): the equation of motion of a sphere rolling on a fixed horizontal plane under an external force →F and torque →K\).
Taking the reaction at the plane to be →R (and note that this can be in any upward direction, not in general vertical), we have
Md→V/dt=→F+→RId→Ω/dt=→K−a→n×→R
The constraint equation, differentiated, gives ˙→V=a˙→Ω×→n, so the first equation can be written
Ma˙→Ω×→n=→F+→R
then substituting ˙→Ω from the second equation,
(I/aM)(→F+→R)=→K×→n−a→R+a→n(→n⋅→R)
This equation gives the components of the reaction force as functions of the external force and couple: the velocities have been eliminated. So we can now put →R in the first equation of motion giving the translational acceleration in terms of the external force and torque. Note that any vertical component of the torque →K will not affect the reaction at the plane →R (it would just spin the ball about the point of contact) so we have, using I=25Ma2.
Rx=57(Ky/a)−27Fx,Ry=−57(Kx/a)−27Fy
and substitution in the original equations of motion gives
dVxdt=57M(Fx+Kya)dVydt=57M(Fy−Kxa)
Exercise: interpret this for the zero torque case, and for the zero force case.
Landau goes on to solve three statics problems which could be in an introductory physics course. We'll skip them.


