5.5: Uniform Circular Motion
- Last updated
- Jun 17, 2019
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 18139
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
Learning Objectives
- Solve for the centripetal acceleration of an object moving on a circular path.
- Use the equations of circular motion to find the position, velocity, and acceleration of a particle executing circular motion.
- Explain the differences between centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration resulting from nonuniform circular motion.
- Evaluate centripetal and tangential acceleration in nonuniform circular motion, and find the total acceleration vector.
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors.
Centripetal Acceleration
In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration. However, in two- and three-dimensional kinematics, even if the speed is a constant, a particle can have acceleration if it moves along a curved trajectory such as a circle. In this case the velocity vector is changing, or d→vdt ≠ 0. This is shown in Figure 5.5.1. As the particle moves counterclockwise in time Δt on the circular path, its position vector moves from →r(t) to →r(t+Δt). The velocity vector has constant magnitude and is tangent to the path as it changes from →v(t) to →v(t+Δt), changing its direction only. Since the velocity vector →v(t) is perpendicular to the position vector →r(t), the triangles formed by the position vectors and Δ→r, and the velocity vectors and Δ→v are similar. Furthermore, since
|→r(t)|=|→r(t+Δt)|
and
|→v(t)|=|→v(t+Δt)|,
the two triangles are isosceles. From these facts we can make the assertion
Δvv=Δrr
or
Δv=vrΔr.
We can find the magnitude of the acceleration from
a=limΔt→0(ΔvΔt)=vr(limΔt→0ΔrΔt)=v2r.
The direction of the acceleration can also be found by noting that as Δt and therefore Δθ approach zero, the vector Δ→v approaches a direction perpendicular to →v. In the limit Δt→0, Δ→v is perpendicular to →v. Since →v is tangent to the circle, the acceleration d→vdt points toward the center of the circle. Summarizing, a particle moving in a circle at a constant speed has an acceleration with magnitude
ac=v2r.
The direction of the acceleration vector is toward the center of the circle (Figure 5.5.2). This is a radial acceleration and is called the centripetal acceleration, which is why we give it the subscript c. The word centripetal comes from the Latin words centrum (meaning “center”) and petere (meaning to seek”), and thus takes the meaning “center seeking.”
Let’s investigate some examples that illustrate the relative magnitudes of the velocity, radius, and centripetal acceleration.
Example 5.5.1: Creating an Acceleration of 1 g
A jet is flying at 134.1 m/s along a straight line and makes a turn along a circular path level with the ground. What does the radius of the circle have to be to produce a centripetal acceleration of 1 g on the pilot and jet toward the center of the circular trajectory?
Strategy
Given the speed of the jet, we can solve for the radius of the circle in the expression for the centripetal acceleration.
Solution
Set the centripetal acceleration equal to the acceleration of gravity: 9.8 m/s2 = v2r.
Solving for the radius, we find
r=(134.1m/s)29.8m/s2=1835m=1.835km.
Significance
To create a greater acceleration than g on the pilot, the jet would either have to decrease the radius of its circular trajectory or increase its speed on its existing trajectory or both.
Exercise 4.5
A flywheel has a radius of 20.0 cm. What is the speed of a point on the edge of the flywheel if it experiences a centripetal acceleration of 900.0 cm/s2?
Centripetal acceleration can have a wide range of values, depending on the speed and radius of curvature of the circular path. Typical centripetal accelerations are given in Table 5.5.1.
| Object | Centripetal Acceleration (m/s2 or factors of g) |
|---|---|
| Earth around the Sun | 5.93 x 10-3 |
| Moon around the Earth | 2.73 x 10-3 |
| Satellite in geosynchronous orbit | 0.233 |
| Outer edge of a CD when playing | 5.75 |
| Jet in a barrel roll | (2-3 g) |
| Roller coaster | (5 g) |
| Electron orbiting a proton in a simple Bohr model of the atom | 9.0 x 1022 |
Equations of Motion for Uniform Circular Motion
A particle executing circular motion can be described by its position vector →r(t). Figure 5.5.3 shows a particle executing circular motion in a counterclockwise direction. As the particle moves on the circle, its position vector sweeps out the angle θ with the x-axis. Vector →r(t) making an angle θ with the x-axis is shown with its components along the x- and y-axes. The magnitude of the position vector is A=|→r(t)| and is also the radius of the circle, so that in terms of its components,
→r(t)=Acosωˆi+Asinωtˆj.
Here, ω is a constant called the angular frequency of the particle. The angular frequency has units of radians (rad) per second and is simply the number of radians of angular measure through which the particle passes per second. The angle θ that the position vector has at any particular time is ωt.
If T is the period of motion, or the time to complete one revolution (2πrad), then
Velocity and acceleration can be obtained from the position function by differentiation:
→v(t)=d→r(t)dt=−Aωsinωtˆi+Aωcosωtˆj.
It can be shown from Figure 5.5.3 that the velocity vector is tangential to the circle at the location of the particle, with magnitude Aω. Similarly, the acceleration vector is found by differentiating the velocity:
→a(t)=d→v(t)dt=−Aω2cosωtˆi−Aω2sinωtˆj.
From this equation we see that the acceleration vector has magnitude Aω2 and is directed opposite the position vector, toward the origin, because →a(t) = −ω2→r(t).
Example 5.5.2: Circular Motion of a Proton
A proton has speed 5 x 106 m/s and is moving in a circle in the xy plane of radius r = 0.175 m. What is its position in the xy plane at time t = 2.0 x 10−7 s = 200 ns? At t = 0, the position of the proton is 0.175 m ˆi and it circles counterclockwise. Sketch the trajectory.
Solution
From the given data, the proton has period and angular frequency:
T=2πrv=2π(0.175m)5.0×106m/s=2.20×10−7s
ω=2πT=2π2.20×10−7s=2.856×107rad/s.
The position of the particle at t = 2.0 x 10−7 s with A = 0.175 m is
→r(2.0×10−7s)=Acosω(2.0×10−7s)ˆi+Asinω(2.0×10−7s)ˆjm=0.175cos(2.856×107rad/s)(2.0×10−7s)ˆi+0.175sin(2.856×107rad/s)(2.0×10−7s)ˆjm=0.175cos(5.712rad)ˆi+0.175sin(5.172rad)ˆjm=0.147ˆi−0.095ˆjm.
From this result we see that the proton is located slightly below the x-axis. This is shown in Figure 5.5.4.
Significance
We picked the initial position of the particle to be on the x-axis. This was completely arbitrary. If a different starting position were given, we would have a different final position at t = 200 ns.
Nonuniform Circular Motion
Circular motion does not have to be at a constant speed. A particle can travel in a circle and speed up or slow down, showing an acceleration in the direction of the motion.
In uniform circular motion, the particle executing circular motion has a constant speed and the circle is at a fixed radius. If the speed of the particle is changing as well, then we introduce an additional acceleration in the direction tangential to the circle. Such accelerations occur at a point on a top that is changing its spin rate, or any accelerating rotor. In Displacement and Velocity Vectors we showed that centripetal acceleration is the time rate of change of the direction of the velocity vector. If the speed of the particle is changing, then it has a tangential acceleration that is the time rate of change of the magnitude of the velocity:
aT=d|→v|dt.
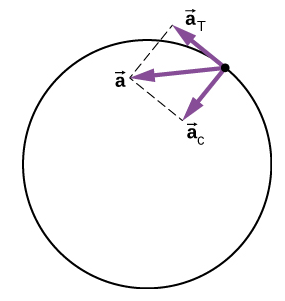
The direction of tangential acceleration is tangent to the circle whereas the direction of centripetal acceleration is radially inward toward the center of the circle. Thus, a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations:
→a=→ac+→aT.
The acceleration vectors are shown in Figure 5.5.5. Note that the two acceleration vectors →ac and →aT are perpendicular to each other, with →ac in the radial direction and →aT in the tangential direction. The total acceleration →a points at an angle between →ac and →aT.
Example 5.5.3: Total Acceleration during Circular Motion
A particle moves in a circle of radius r = 2.0 m. During the time interval from t = 1.5 s to t = 4.0 s its speed varies with time according to
v(t)=c1−c2t2,c1=4.0m/s,c2=6.0m⋅s.
What is the total acceleration of the particle at t = 2.0 s?
Strategy
We are given the speed of the particle and the radius of the circle, so we can calculate centripetal acceleration easily. The direction of the centripetal acceleration is toward the center of the circle. We find the magnitude of the tangential acceleration by taking the derivative with respect to time of |v(t)| using Equation ??? and evaluating it at t = 2.0 s. We use this and the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration to find the total acceleration.
Solution
Centripetal acceleration is
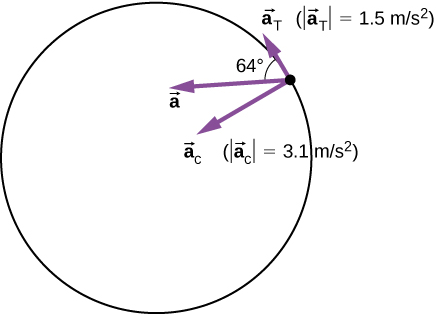
v(2.0s)=(4.0−6.0(2.0)2)m/s=2.5m/s
ac=v2r=(2.5m/s)22.0m=3.1m/s2
directed toward the center of the circle. Tangential acceleration is
aT=|d→vdt|=2c2t3=12.0(2.0)3m/s2=1.5m/s2.
Total acceleration is
|→a|=√3.12+1.52m/s2=3.44m/s2
and θ = tan−1 (3.11.5) = 64° from the tangent to the circle. See Figure 5.5.6.
Significance
The directions of centripetal and tangential accelerations can be described more conveniently in terms of a polar coordinate system, with unit vectors in the radial and tangential directions. This coordinate system, which is used for motion along curved paths, is discussed in detail later in the book.


