6.7: Real-World Examples of Chemical Reactions and Their Types
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
Real-World Examples of Chemical Reactions and Their Types
1. Synthesis Reaction: Formation of Ammonia
Scenario: The industrial production of ammonia (NH₃) through the Haber process is a crucial chemical reaction used to manufacture fertilizers.
Chemical Reaction:

Explanation: In this synthesis reaction, nitrogen gas (N₂) combines with hydrogen gas (H₂) to form ammonia (NH₃). This process is critical for producing fertilizers that support global agriculture.
2. Decomposition Reaction: Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
Scenario: Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is commonly used as a disinfectant and bleach. It decomposes over time or when catalyzed by an enzyme called catalase.
Chemical Reaction:

Explanation: In this decomposition reaction, hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water (H₂O) and oxygen gas (O₂). This reaction is utilized in disinfecting wounds, where the oxygen released helps kill bacteria.
3. Single Replacement Reaction: Zinc and Hydrochloric Acid
Scenario: Zinc (Zn) is often used in galvanizing processes to protect iron from rusting. When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it demonstrates a single replacement reaction.
Chemical Reaction:.
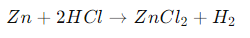
Explanation: In this single replacement reaction, zinc displaces hydrogen in hydrochloric acid, forming zinc chloride (ZnCl₂) and releasing hydrogen gas (H₂). This reaction can be observed in laboratory demonstrations involving metal-acid reactions.
4. Double Replacement Reaction: Reaction Between Sodium Chloride and Silver Nitrate
Scenario: A classic laboratory experiment involves mixing sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO₃) to observe the formation of a precipitate.
Chemical Reaction:
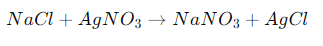
Explanation: In this double replacement reaction, the cations and anions of the reactants exchange places, forming sodium nitrate (NaNO₃) and silver chloride (AgCl). The silver chloride forms a white precipitate, demonstrating the reaction visually.
5. Combustion Reaction: Burning of Propane
Scenario: Propane (C₃H₈) is commonly used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and in portable stoves.
Chemical Reaction:

Explanation: In this combustion reaction, propane reacts with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and energy in the form of heat and light. This exothermic reaction is essential for everyday heating and cooking applications.
Summary
These real-world examples illustrate the different types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion. Each type of reaction plays a vital role in various industrial, laboratory, and everyday processes, showcasing the diverse and impactful nature of chemical transformations.

